The SMIF interface can be used to transmit different types of commands.
Each command has different phases: command, dummy cycles, and transmit and receive data which require separate APIs.
During the time that Slave Select line is active (LOW) the clock signal (CLK) is toggled while command information is first transferred on the data (IO) signals from the master to the slave. The clock continues to toggle during any period required for information access in the slave. The clock continues to toggle during the transfer of read data from the slave to the master or write data from the master to the slave. When the master has transferred the desired amount of data, the master drives the Slave Select line inactive (HIGH). Basic flow for read/write commands using Cy_SMIF_TransmitCommand, Cy_SMIF_TransmitData, Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData and Cy_SMIF_SendDummyCycles with a Quad SPI interface.
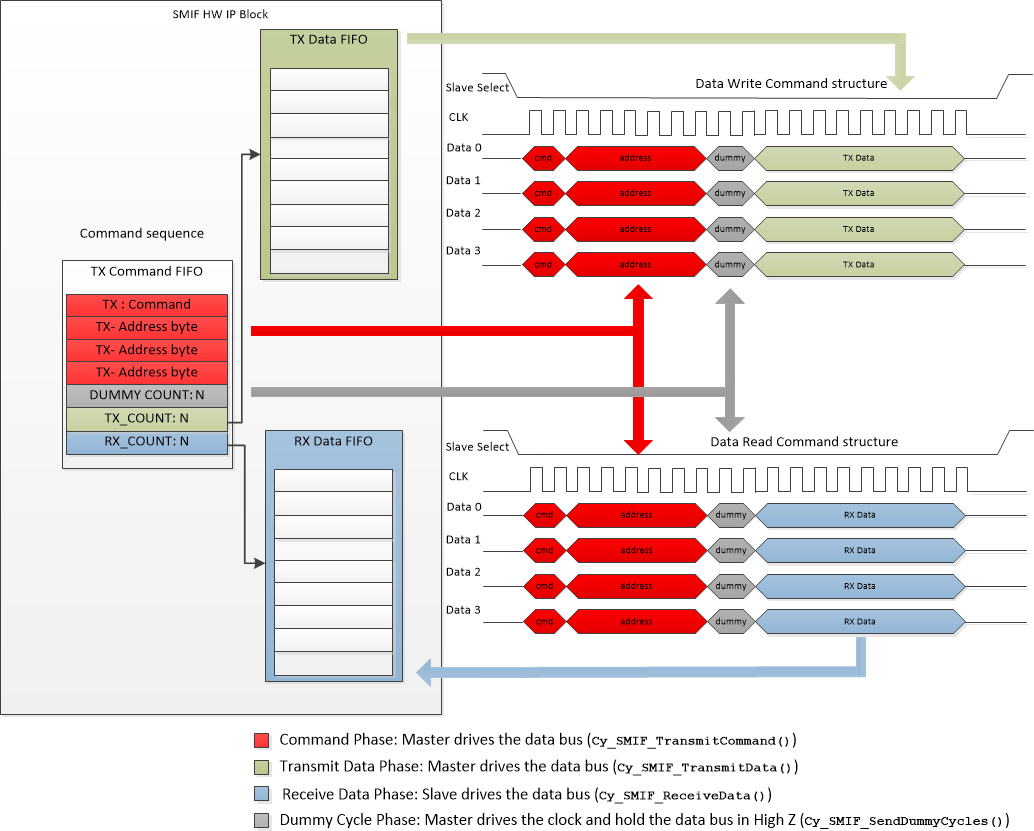
The sequence of the PDL functions required in a read or write transaction is: Cy_SMIF_TransmitCommand() -> Cy_SMIF_SendDummyCycles() -> Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData() / Cy_SMIF_TransmitData() -> Cy_SMIF_BusyCheck(). The address is sent as part of the Cy_SMIF_TransmitCommand() function. No separate function call is required.
API Reference | |
| Low Power Callback | |
| The driver supports SysPm callback for Deep Sleep and Hibernate transition. | |
Functions | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_Init (SMIF_Type *base, cy_stc_smif_config_t const *config, uint32_t timeout, cy_stc_smif_context_t *context) |
| This function initializes the SMIF block as a communication block. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_DllConfig (volatile SMIF_Type *base, cy_stc_smif_config_t const *config, cy_stc_smif_context_t *context) |
| This function configures the DLL for use, per the SMIF configuration structure parameters. More... | |
| void | Cy_SMIF_DeInit (SMIF_Type *base) |
| This function de-initializes the SMIF block to default values. More... | |
| void | Cy_SMIF_SetDataSelect (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_slave_select_t slaveSelect, cy_en_smif_data_select_t dataSelect) |
| This function configures the data select option for a specific slave. More... | |
| void | Cy_SMIF_SetMode (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_mode_t mode) |
| Sets the mode of operation for the SMIF. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_mode_t | Cy_SMIF_GetMode (SMIF_Type const *base) |
| Reads the mode of operation for the SMIF. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_TransmitCommand (SMIF_Type *base, uint8_t cmd, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t cmdTxfrWidth, uint8_t const cmdParam[], uint32_t paramSize, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t paramTxfrWidth, cy_en_smif_slave_select_t slaveSelect, uint32_t completeTxfr, cy_stc_smif_context_t const *context) |
| This function transmits a command byte followed by a parameter which is typically an address field. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_TransmitData (SMIF_Type *base, uint8_t const *txBuffer, uint32_t size, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t transferWidth, cy_smif_event_cb_t TxCompleteCb, cy_stc_smif_context_t *context) |
| This function is used to transmit data using the SMIF interface. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_TransmitDataBlocking (SMIF_Type *base, uint8_t const *txBuffer, uint32_t size, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t transferWidth, cy_stc_smif_context_t const *context) |
| This function implements the transmit data phase in the memory command. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData (SMIF_Type *base, uint8_t *rxBuffer, uint32_t size, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t transferWidth, cy_smif_event_cb_t RxCompleteCb, cy_stc_smif_context_t *context) |
| This function implements the receive data phase in the memory command. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_ReceiveDataBlocking (SMIF_Type *base, uint8_t *rxBuffer, uint32_t size, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t transferWidth, cy_stc_smif_context_t const *context) |
| This function implements the receive data phase in the memory command. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_SendDummyCycles (SMIF_Type *base, uint32_t cycles) |
| This function sends dummy-clock cycles. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_txfr_status_t | Cy_SMIF_GetTransferStatus (SMIF_Type const *base, cy_stc_smif_context_t const *context) |
| This function provides the status of the transfer. More... | |
| void | Cy_SMIF_Enable (SMIF_Type *base, cy_stc_smif_context_t *context) |
| Enables the operation of the SMIF block. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_TransmitCommand_Ext (SMIF_Type *base, uint16_t cmd, bool isCommand2byte, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t cmdTxfrWidth, cy_en_smif_data_rate_t cmdDataRate, uint8_t const cmdParam[], uint32_t paramSize, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t paramTxfrWidth, cy_en_smif_data_rate_t paramDataRate, cy_en_smif_slave_select_t slaveSelect, uint32_t completeTxfr, cy_stc_smif_context_t const *context) |
| This function transmits a command byte followed by a parameter which is typically an address field. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_TransmitData_Ext (SMIF_Type *base, uint8_t const *txBuffer, uint32_t size, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t transferWidth, cy_en_smif_data_rate_t dataDataRate, cy_smif_event_cb_t TxCmpltCb, cy_stc_smif_context_t *context) |
| This function is used to transmit data using the SMIF interface. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_TransmitDataBlocking_Ext (SMIF_Type *base, uint8_t const *txBuffer, uint32_t size, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t transferWidth, cy_en_smif_data_rate_t dataDataRate, cy_stc_smif_context_t const *context) |
| This function implements the transmit data phase in the memory command. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData_Ext (SMIF_Type *base, uint8_t *rxBuffer, uint32_t size, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t transferWidth, cy_en_smif_data_rate_t dataRate, cy_smif_event_cb_t RxCmpltCb, cy_stc_smif_context_t *context) |
| This function implements the receive data phase in the memory command. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_ReceiveDataBlocking_Ext (SMIF_Type *base, uint8_t *rxBuffer, uint32_t size, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t transferWidth, cy_en_smif_data_rate_t dataRate, cy_stc_smif_context_t const *context) |
| This function implements the receive data phase in the memory command. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_SendDummyCycles_Ext (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t transferWidth, cy_en_smif_data_rate_t dataRate, uint32_t cycles) |
| This function sends dummy-clock cycles. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_SendDummyCycles_With_RWDS (SMIF_Type *base, bool read_rwds, bool refresh_indicator, uint32_t cycles) |
| This function sends dummy-clock cycles and observes additional input data signal RWDS. More... | |
| void | Cy_SMIF_DeviceTransfer_SetMergeTimeout (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_slave_select_t slave, cy_en_smif_merge_timeout_t timeout) |
| This function enables merging continuous transfers over XIP so that the overhead of transferring command and address will not be there for reading consecutive addresses. More... | |
| void | Cy_SMIF_DeviceTransfer_ClearMergeTimeout (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_slave_select_t slave) |
| This function disables continuous transfer merging. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_Set_DelayTapSel (SMIF_Type *base, uint8_t tapSel) |
| This function sets delay tap number for the SMIF master clock which is common for all memory devices connected. More... | |
| uint8_t | Cy_SMIF_Get_DelayTapSel (SMIF_Type *base) |
| This function returns delay tap number which has been set for the SMIF. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_Set_Sdl_DelayTapSel (SMIF_CORE_DEVICE_Type *smif_device_base, uint8_t tapSel) |
| This function sets the SDL (slave clock) delay tap number for the SMIF (common for all its devices). More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | Cy_SMIF_Disable (SMIF_Type *base) |
| Disables the operation of the SMIF block. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | Cy_SMIF_SetInterruptMask (SMIF_Type *base, uint32_t interrupt) |
| This function is used to set an interrupt mask for the SMIF Interrupt. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t | Cy_SMIF_GetInterruptMask (SMIF_Type const *base) |
| This function is used to read an interrupt mask for the SMIF Interrupt. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t | Cy_SMIF_GetInterruptStatusMasked (SMIF_Type const *base) |
| This function is used to read an active masked interrupt. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t | Cy_SMIF_GetInterruptStatus (SMIF_Type const *base) |
| This function is used to read an active interrupt. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | Cy_SMIF_SetInterrupt (SMIF_Type *base, uint32_t interrupt) |
| This function is used to set an interrupt source. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | Cy_SMIF_ClearInterrupt (SMIF_Type *base, uint32_t interrupt) |
| This function is used to clear an interrupt source. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | Cy_SMIF_SetTxFifoTriggerLevel (SMIF_Type *base, uint32_t level) |
| This function is used to set a trigger level for the TX FIFO. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | Cy_SMIF_SetRxFifoTriggerLevel (SMIF_Type *base, uint32_t level) |
| This function is used to set a trigger level for the RX FIFO. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t | Cy_SMIF_GetCmdFifoStatus (SMIF_Type const *base) |
| This function is used to read the status of the CMD FIFO. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t | Cy_SMIF_GetTxFifoStatus (SMIF_Type const *base) |
| This function is used to read the status of the TX FIFO. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t | Cy_SMIF_GetRxFifoStatus (SMIF_Type const *base) |
| This function is used to read the status of the RX FIFO. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_Encrypt (SMIF_Type *base, uint32_t address, uint8_t data[], uint32_t size, cy_stc_smif_context_t const *context) |
| Uses the Encryption engine to create an encrypted result when the input, key and data arrays are provided. More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE bool | Cy_SMIF_BusyCheck (SMIF_Type const *base) |
| This function provides the status of the IP block (False - not busy, True - busy). More... | |
| __STATIC_INLINE void | Cy_SMIF_Interrupt (SMIF_Type *base, cy_stc_smif_context_t *context) |
| The Interrupt Service Routine for the SMIF. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_CacheEnable (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_cache_t cacheType) |
| This function is used to enable the fast cache, the slow cache or both. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_CacheDisable (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_cache_t cacheType) |
| This function is used to disable the fast cache, the slow cache or both. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_CachePrefetchingEnable (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_cache_t cacheType) |
| This function is used to enable pre-fetching for the fast cache, the slow cache or both. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_CachePrefetchingDisable (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_cache_t cacheType) |
| This function is used to disable pre-fetching for the fast cache, the slow cache or both. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_CacheInvalidate (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_cache_t cacheType) |
| This function is used to invalidate/clear the fast cache, the slow cache or both. More... | |
| void | Cy_SMIF_SetCryptoKey (SMIF_Type *base, uint32_t *key) |
| Sets the AES-128 encryption key into SMIF crypto registers. More... | |
| void | Cy_SMIF_SetCryptoIV (SMIF_Type *base, uint32_t *nonce) |
| Sets the 96 bit initialization vector (nonce) into SMIF crypto registers. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_SetCryptoEnable (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_slave_select_t slaveId) |
| Enables SMIF encryption. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_SetCryptoDisable (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_slave_select_t slaveId) |
| Disables SMIF encryption. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_IsCryptoEnabled (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_slave_select_t slaveId, bool *crypto_status) |
| Checks the status of encryption for the selected slave device. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_ConvertSlaveSlotToIndex (cy_en_smif_slave_select_t ss, uint32_t *device_idx) |
| Converts Slave Select enum to the device index. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_SetRxCaptureMode (SMIF_Type *base, cy_en_smif_capture_mode_t mode, cy_en_smif_slave_select_t slaveId) |
| This function sets the Rx Capture mode setting for SMIF IP block instance. More... | |
| bool | Cy_SMIF_IsBridgeOn (SMIF_Base_Type *base) |
| This function is used to check the bridge enable state. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_Bridge_Enable (SMIF_Base_Type *base, bool enable) |
| This function is used to enable/disable Bridge. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_SetMasterDLP (SMIF_Type *base, uint16 dlp, uint8_t size) |
| This function sets the data learning pattern. More... | |
| uint16_t | Cy_SMIF_GetMasterDLP (SMIF_Type *base) |
| This function gets the data learning pattern configured. More... | |
| uint8_t | Cy_SMIF_GetMasterDLPSize (SMIF_Type *base) |
| This function gets the data learning pattern size configured. More... | |
| uint8_t | Cy_SMIF_GetTapNumCapturedCorrectDLP (SMIF_Type *base, uint8_t bit) |
| This function gets number of delay taps used for specified data line. More... | |
| uint32_t | CY_SMIF_GetDelayTapsNumber (volatile void *base) |
| This function returns tap number which the SMIF IP has. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_InitCache (SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type *base, const cy_stc_smif_cache_config_t *cache_config) |
| This function initializes SMIF internal CACHE with user provided configuration cy_stc_smif_cache_config_t. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_Clean_All_Cache (SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type *base) |
| This function cleans complete SMIF internal CACHE. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_Invalidate_All_Cache (SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type *base) |
| This function invalidates complete SMIF internal CACHE. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_Clean_And_Invalidate_All_Cache (SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type *base) |
| This function cleans and invalidates complete SMIF internal CACHE. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_Clean_Cache_by_Addr (SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type *base, bool is_secure_view, uint32_t address, uint32_t size) |
| This function cleans cache using the address and size specified by user. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_Invalidate_Cache_by_Addr (SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type *base, bool is_secure_view, uint32_t address, uint32_t size) |
| This function invalidates cache using the address and size specified by user. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_Clean_And_Invalidate_Cache_by_Addr (SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type *base, bool is_secure_view, uint32_t address, uint32_t size) |
| This function cleans and invalidates cache using the address and size specified by user. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t | Cy_SMIF_IsCacheEnabled (SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type *base, bool *cache_status) |
| This function checks whether Cache is enabled or not. More... | |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_Init | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_stc_smif_config_t const * | config, | ||
| uint32_t | timeout, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t * | context | ||
| ) |
This function initializes the SMIF block as a communication block.
The user must ensure that the SMIF interrupt is disabled while this function is called. Enabling the interrupts can lead to triggering in the middle of the initialization operation, which can lead to erroneous initialization.
As parameters, this function takes the SMIF register base address and a context structure along with the configuration needed for the SMIF block, stored in a config.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| config | Passes a configuration structure that configures the SMIF block for operation. |
| timeout | A timeout in microseconds for blocking APIs in use. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_DllConfig | ( | volatile SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_stc_smif_config_t const * | config, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t * | context | ||
| ) |
This function configures the DLL for use, per the SMIF configuration structure parameters.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| config | Passes a configuration structure that configures the SMIF block for operation, here specifically it is used to configure the DLL. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| void Cy_SMIF_DeInit | ( | SMIF_Type * | base | ) |
This function de-initializes the SMIF block to default values.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| void Cy_SMIF_SetDataSelect | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_slave_select_t | slaveSelect, | ||
| cy_en_smif_data_select_t | dataSelect | ||
| ) |
This function configures the data select option for a specific slave.
The selection provides pre-set combinations for connecting the SMIF data lines to the GPIOs.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| slaveSelect | The slave device ID. This number is either CY_SMIF_SLAVE_SELECT_0 or CY_SMIF_SLAVE_SELECT_1 or CY_SMIF_SLAVE_SELECT_2 or CY_SMIF_SLAVE_SELECT_3 (cy_en_smif_slave_select_t). It defines the slave select line to be used during the transmission. |
| dataSelect | This parameter selects the data select option. cy_en_smif_data_select_t |
| void Cy_SMIF_SetMode | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_mode_t | mode | ||
| ) |
Sets the mode of operation for the SMIF.
The mode of operation can be the XIP mode where the slave devices are mapped as memories and are directly accessed from the PSoC register map. In the MMIO mode, the SMIF block acts as a simple SPI engine. MMIO mode and XIP modes are mutually exclusive. SMIF IP Version 3 and above support MMIO mode transactions even when XIP mode is enabled. However, user has to ensure that XIP transaction is not issued during an ongoing MMIO transaction. Rather wait for MMIO transaction to complete since few MMIO operations make external flash busy and it cannot respond to XIP read transaction.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| mode | The mode of the SMIF operation. |
| cy_en_smif_mode_t Cy_SMIF_GetMode | ( | SMIF_Type const * | base | ) |
Reads the mode of operation for the SMIF.
The mode of operation can be the XIP mode where the slave devices are mapped as memories and are directly accessed from the PSoC register map. In the MMIO mode, the SMIF block acts as a simple SPI engine.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_TransmitCommand | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint8_t | cmd, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | cmdTxfrWidth, | ||
| uint8_t const | cmdParam[], | ||
| uint32_t | paramSize, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | paramTxfrWidth, | ||
| cy_en_smif_slave_select_t | slaveSelect, | ||
| uint32_t | completeTxfr, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t const * | context | ||
| ) |
This function transmits a command byte followed by a parameter which is typically an address field.
The transfer is implemented using the TX FIFO. This function also asserts the slave select line. A command to a memory device generally starts with a command byte transmission. This function sets up the slave lines for the rest of the command structure. The Cy_SMIF_TransmitCommand is called before Cy_SMIF_TransmitData or Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData is called. When enabled, the completeTxfr parameter in the function will de-assert the slave select line at the end of the function execution.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| cmd | The command byte to be transmitted. |
| cmdTxfrWidth | The width of command byte transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| cmdParam | This is the pointer to an array that has bytes to be transmitted after the command byte. Typically, this field has the address bytes associated with the memory command. |
| paramSize | The size of the cmdParam array. |
| paramTxfrWidth | The width of parameter transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| slaveSelect | Denotes the number of the slave device to which the transfer is made. (0, 1, 2 or 4 - the bit defines which slave to enable) Two-bit enable is possible only for the double quad SPI mode. |
| completeTxfr | Specifies if the slave select line must be de-asserted after transferring the last byte in the parameter array. Typically, this field is set to 0 when this function succeed through Cy_SMIF_TransmitData or Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_TransmitData | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint8_t const * | txBuffer, | ||
| uint32_t | size, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | transferWidth, | ||
| cy_smif_event_cb_t | TxCompleteCb, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t * | context | ||
| ) |
This function is used to transmit data using the SMIF interface.
This function uses the TX Data FIFO to implement the transmit functionality. The function sets up an interrupt to trigger the TX Data FIFO and uses that interrupt to fill the TX Data FIFO until all the data is transmitted. At the end of the transmission, the TxCompleteCb is executed.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| txBuffer | The pointer to the data to be transferred. If this pointer is a NULL, then the function does not enable the interrupt. This use case is typically used when the FIFO is handled outside the interrupt and is managed in either a polling-based code or a DMA. The user would handle the FIFO management in a DMA or a polling-based code. |
| size | The size of txBuffer. Must be > 0 and not greater than 65536. |
| transferWidth | The width of transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| TxCompleteCb | The callback executed at the end of a transmission. NULL interpreted as no callback. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_TransmitDataBlocking | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint8_t const * | txBuffer, | ||
| uint32_t | size, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | transferWidth, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t const * | context | ||
| ) |
This function implements the transmit data phase in the memory command.
The data is transmitted using the Tx Data FIFO and the TX_COUNT command. This function blocks until completion. The function does not use the interrupts and will use CPU to monitor the FIFO status and move data accordingly. The function returns only on completion.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| txBuffer | The pointer to the data to be transferred. If this pointer is a NULL, then the function does not fill TX_FIFO. The user would handle the FIFO management in a DMA or a polling-based code. |
| size | The size of txBuffer. Must be > 0 and not greater than 65536. |
| transferWidth | The width of transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint8_t * | rxBuffer, | ||
| uint32_t | size, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | transferWidth, | ||
| cy_smif_event_cb_t | RxCompleteCb, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t * | context | ||
| ) |
This function implements the receive data phase in the memory command.
The data is received into the RX Data FIFO using the RX_COUNT command. This function sets up the interrupt to trigger on the RX Data FIFO level, and the data is fetched from the RX Data FIFO to the rxBuffer as it gets filled. This function does not block until completion. The completion will trigger the call back function.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| rxBuffer | The pointer to the variable where the receive data is stored. If this pointer is a NULL, then the function does not enable the interrupt. This use case is typically used when the FIFO is handled outside the interrupt and is managed in either a polling-based code or a DMA. The user would handle the FIFO management in a DMA or a polling-based code. |
| size | The size of data to be received. Must be > 0 and not greater than 65536. |
| transferWidth | The width of transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| RxCompleteCb | The callback executed at the end of a reception. NULL interpreted as no callback. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_ReceiveDataBlocking | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint8_t * | rxBuffer, | ||
| uint32_t | size, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | transferWidth, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t const * | context | ||
| ) |
This function implements the receive data phase in the memory command.
The data is received into the RX Data FIFO using the RX_COUNT command. This function blocks until completion. The function does not use the interrupts and will use CPU to monitor the FIFO status and move data accordingly. The function returns only on completion.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| rxBuffer | The pointer to the variable where the receive data is stored. If this pointer is a NULL, then the function does not enable the interrupt. This use case is typically used when the FIFO is handled outside the interrupt and is managed in either a polling-based code or a DMA. The user would handle the FIFO management in a DMA or a polling-based code. |
| size | The size of data to be received. Must be > 0 and not greater than 65536. |
| transferWidth | The width of transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_SendDummyCycles | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint32_t | cycles | ||
| ) |
This function sends dummy-clock cycles.
The data lines are tri-stated during the dummy cycles.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| cycles | The number of dummy cycles. Must be > 0 and not greater than 65536. |
| cy_en_smif_txfr_status_t Cy_SMIF_GetTransferStatus | ( | SMIF_Type const * | base, |
| cy_stc_smif_context_t const * | context | ||
| ) |
This function provides the status of the transfer.
This function is used to poll for the status of the TransmitData or receiveData function. When this function is called to determine the status of ongoing Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData() or Cy_SMIF_TransmitData(), the returned status is only valid if the functions passed a non-NULL buffer to transmit or receive respectively. If the pointer passed to Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData() or Cy_SMIF_TransmitData() is a NULL, then the code/DMA outside this driver will take care of the transfer and the Cy_GetTxfrStatus() will return an erroneous result.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| void Cy_SMIF_Enable | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_stc_smif_context_t * | context | ||
| ) |
Enables the operation of the SMIF block.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_TransmitCommand_Ext | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint16_t | cmd, | ||
| bool | isCommand2byte, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | cmdTxfrWidth, | ||
| cy_en_smif_data_rate_t | cmdDataRate, | ||
| uint8_t const | cmdParam[], | ||
| uint32_t | paramSize, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | paramTxfrWidth, | ||
| cy_en_smif_data_rate_t | paramDataRate, | ||
| cy_en_smif_slave_select_t | slaveSelect, | ||
| uint32_t | completeTxfr, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t const * | context | ||
| ) |
This function transmits a command byte followed by a parameter which is typically an address field.
The transfer is implemented using the TX FIFO. This function also asserts the slave select line. A command to a memory device generally starts with a command byte transmission. This function sets up the slave lines for the rest of the command structure. The Cy_SMIF_TransmitCommand_Ext is called before Cy_SMIF_TransmitData_Ext or Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData_Ext is called. When enabled, the completeTxfr parameter in the function will de-assert the slave select line at the end of the function execution.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| cmd | The command byte to be transmitted. |
| isCommand2byte | isCommand2byte |
| cmdTxfrWidth | The width of command byte transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| cmdDataRate | cmdDataRate |
| cmdParam | This is the pointer to an array that has bytes to be transmitted after the command byte. Typically, this field has the address bytes associated with the memory command. |
| paramSize | The size of the cmdParam array. |
| paramTxfrWidth | The width of parameter transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| paramDataRate | paramDataRate |
| slaveSelect | Denotes the number of the slave device to which the transfer is made. (0, 1, 2 or 4 - the bit defines which slave to enable) Two-bit enable is possible only for the Double Quad SPI mode. |
| completeTxfr | Specifies if the slave select line must be de-asserted after transferring the last byte in the parameter array. Typically, this field is set to 0 when this function succeed through Cy_SMIF_TransmitData_Ext or Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData_Ext. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_TransmitData_Ext | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint8_t const * | txBuffer, | ||
| uint32_t | size, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | transferWidth, | ||
| cy_en_smif_data_rate_t | dataDataRate, | ||
| cy_smif_event_cb_t | TxCmpltCb, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t * | context | ||
| ) |
This function is used to transmit data using the SMIF interface.
This function uses the TX Data FIFO to implement the transmit functionality. The function sets up an interrupt to trigger the TX Data FIFO and uses that interrupt to fill the TX Data FIFO until all the data is transmitted. At the end of the transmission, the TxCmpltCb is executed.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| txBuffer | The pointer to the data to be transferred. If this pointer is a NULL, then the function does not enable the interrupt. This use case is typically used when the FIFO is handled outside the interrupt and is managed in either a polling-based code or a DMA. The user would handle the FIFO management in a DMA or a polling-based code. |
| size | The size of txBuffer. Must be > 0 and not greater than 65536. |
| transferWidth | The width of transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| dataDataRate | dataDataRate |
| TxCmpltCb | The callback executed at the end of a transmission. NULL interpreted as no callback. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_TransmitDataBlocking_Ext | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint8_t const * | txBuffer, | ||
| uint32_t | size, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | transferWidth, | ||
| cy_en_smif_data_rate_t | dataDataRate, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t const * | context | ||
| ) |
This function implements the transmit data phase in the memory command.
The data is transmitted using the Tx Data FIFO and the TX_COUNT command. This function blocks until completion. The function does not use the interrupts and will use CPU to monitor the FIFO status and move data accordingly. The function returns only on completion.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| txBuffer | The pointer to the data to be transferred. If this pointer is a NULL, then the function does not fill TX_FIFO. The user would handle the FIFO management in a DMA or a polling-based code. |
| size | The size of txBuffer. Must be > 0 and not greater than 65536. |
| transferWidth | The width of transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| dataDataRate | dataDataRate |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_ReceiveData_Ext | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint8_t * | rxBuffer, | ||
| uint32_t | size, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | transferWidth, | ||
| cy_en_smif_data_rate_t | dataRate, | ||
| cy_smif_event_cb_t | RxCmpltCb, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t * | context | ||
| ) |
This function implements the receive data phase in the memory command.
The data is received into the RX Data FIFO using the RX_COUNT command. This function sets up the interrupt to trigger on the RX Data FIFO level, and the data is fetched from the RX Data FIFO to the rxBuffer as it gets filled. This function does not block until completion. The completion will trigger the call back function.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| rxBuffer | The pointer to the variable where the receive data is stored. If this pointer is a NULL, then the function does not enable the interrupt. This use case is typically used when the FIFO is handled outside the interrupt and is managed in either a polling-based code or a DMA. The user would handle the FIFO management in a DMA or a polling-based code. |
| size | The size of data to be received. Must be > 0 and not greater than 65536. |
| transferWidth | The width of transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| dataRate | dataRate |
| RxCmpltCb | The callback executed at the end of a reception. NULL interpreted as no callback. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_ReceiveDataBlocking_Ext | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint8_t * | rxBuffer, | ||
| uint32_t | size, | ||
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | transferWidth, | ||
| cy_en_smif_data_rate_t | dataRate, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t const * | context | ||
| ) |
This function implements the receive data phase in the memory command.
The data is received into the RX Data FIFO using the RX_COUNT command. This function blocks until completion. The function does not use the interrupts and will use CPU to monitor the FIFO status and move data accordingly. The function returns only on completion.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| rxBuffer | The pointer to the variable where the receive data is stored. If this pointer is a NULL, then the function does not enable the interrupt. This use case is typically used when the FIFO is handled outside the interrupt and is managed in either a polling-based code or a DMA. The user would handle the FIFO management in a DMA or a polling-based code. |
| size | The size of data to be received. Must be > 0 and not greater than 65536. |
| transferWidth | The width of transfer cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t. |
| dataRate | dataRate |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_SendDummyCycles_Ext | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_txfr_width_t | transferWidth, | ||
| cy_en_smif_data_rate_t | dataRate, | ||
| uint32_t | cycles | ||
| ) |
This function sends dummy-clock cycles.
The data lines are tri-stated during the dummy cycles.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| transferWidth | |
| dataRate | |
| cycles | The number of dummy cycles. Must be > 0 and not greater than 65536. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_SendDummyCycles_With_RWDS | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| bool | read_rwds, | ||
| bool | refresh_indicator, | ||
| uint32_t | cycles | ||
| ) |
This function sends dummy-clock cycles and observes additional input data signal RWDS.
The data lines are tri-stated during the dummy cycles.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| read_rwds | Indicates whether it is read/write transaction. "true" in case of read. "false" in case of write. |
| refresh_indicator | Dummy cycles are doubled when RWDS refresh indicator is high during CA cycle. (HyperRAM variable latency mode) |
| cycles | The number of dummy cycles. Must be > 0 and not greater than 65536. |
| void Cy_SMIF_DeviceTransfer_SetMergeTimeout | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_slave_select_t | slave, | ||
| cy_en_smif_merge_timeout_t | timeout | ||
| ) |
This function enables merging continuous transfers over XIP so that the overhead of transferring command and address will not be there for reading consecutive addresses.
User can specify a timeout value to specify how long the device would be selected waiting for next incremental address read.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| slave | Holds the slave select line for which merge should be enabled. |
| timeout | (see cy_en_smif_merge_timeout_t) |
| void Cy_SMIF_DeviceTransfer_ClearMergeTimeout | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_slave_select_t | slave | ||
| ) |
This function disables continuous transfer merging.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| slave | Holds the slave select line for which merge should be disabled. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_Set_DelayTapSel | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint8_t | tapSel | ||
| ) |
This function sets delay tap number for the SMIF master clock which is common for all memory devices connected.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block or SMIF_DEVICE block registers. |
| tapSel | delay tap selection to be set |
| uint8_t Cy_SMIF_Get_DelayTapSel | ( | SMIF_Type * | base | ) |
This function returns delay tap number which has been set for the SMIF.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block or SMIF_DEVICE block registers. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_Set_Sdl_DelayTapSel | ( | SMIF_CORE_DEVICE_Type * | smif_device_base, |
| uint8_t | tapSel | ||
| ) |
This function sets the SDL (slave clock) delay tap number for the SMIF (common for all its devices).
It sets both the positive and negative taps to the same value.
| smif_device_base | Holds the base address of the SMIF_DEVICE block registers. |
| tapSel | positive and negative delay tap selection to be set |
| __STATIC_INLINE void Cy_SMIF_Disable | ( | SMIF_Type * | base | ) |
Disables the operation of the SMIF block.
The SMIF block can be disabled only when it is not in the active state. Use the Cy_SMIF_BusyCheck() API to check it before calling this API. Make sure the clock supplied to SMIF block is also disabled before calling this API using Cy_SysClk_ClkHfDisable
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| __STATIC_INLINE void Cy_SMIF_SetInterruptMask | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint32_t | interrupt | ||
| ) |
This function is used to set an interrupt mask for the SMIF Interrupt.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| interrupt | This is the mask for different source options that can be masked. See Interrupt Macros for possible values. |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t Cy_SMIF_GetInterruptMask | ( | SMIF_Type const * | base | ) |
This function is used to read an interrupt mask for the SMIF Interrupt.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t Cy_SMIF_GetInterruptStatusMasked | ( | SMIF_Type const * | base | ) |
This function is used to read an active masked interrupt.
This function can be used in the interrupt service-routine to find which source triggered the interrupt.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t Cy_SMIF_GetInterruptStatus | ( | SMIF_Type const * | base | ) |
This function is used to read an active interrupt.
This status is the unmasked result, so will also show interrupts that will not generate active interrupts.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| __STATIC_INLINE void Cy_SMIF_SetInterrupt | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint32_t | interrupt | ||
| ) |
This function is used to set an interrupt source.
This function can be used to activate interrupts through the software.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| interrupt | An encoded integer with a bit set corresponding to the interrupt to be triggered. See Interrupt Macros for possible values. |
| __STATIC_INLINE void Cy_SMIF_ClearInterrupt | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint32_t | interrupt | ||
| ) |
This function is used to clear an interrupt source.
This function can be used in the user code to clear all pending interrupts.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| interrupt | An encoded integer with a bit set corresponding to the interrupt that must be cleared. See Interrupt Macros for possible values. |
| __STATIC_INLINE void Cy_SMIF_SetTxFifoTriggerLevel | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint32_t | level | ||
| ) |
This function is used to set a trigger level for the TX FIFO.
This value must be an integer between 0 and 7. For the normal mode only. The triggering is active when TX_DATA_FIFO_STATUS <= level.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| level | The trigger level to set (0-8). |
| __STATIC_INLINE void Cy_SMIF_SetRxFifoTriggerLevel | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint32_t | level | ||
| ) |
This function is used to set a trigger level for the RX FIFO.
This value must be an integer between 0 and 7. For the normal mode only. The triggering is active when RX_DATA_FIFOSTATUS > level.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| level | The trigger level to set(0-8). |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t Cy_SMIF_GetCmdFifoStatus | ( | SMIF_Type const * | base | ) |
This function is used to read the status of the CMD FIFO.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t Cy_SMIF_GetTxFifoStatus | ( | SMIF_Type const * | base | ) |
This function is used to read the status of the TX FIFO.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| __STATIC_INLINE uint32_t Cy_SMIF_GetRxFifoStatus | ( | SMIF_Type const * | base | ) |
This function is used to read the status of the RX FIFO.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_Encrypt | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint32_t | address, | ||
| uint8_t | data[], | ||
| uint32_t | size, | ||
| cy_stc_smif_context_t const * | context | ||
| ) |
Uses the Encryption engine to create an encrypted result when the input, key and data arrays are provided.
The AES-128 encryption of the address with the key, fetching the result and XOR with the data array are all done in the function. The operational scheme is the following: data = XOR(AES128(address, key), data) Decryption is done using the input data-array identically to the encryption. In the XIP mode, encryption and decryption are done without calling this function. The operational scheme in the XIP mode is the same. The address parameter in the XIP mode equals the actual address in the PSoC memory map. The SMIF encryption engine is designed for code storage. For data storage, the encryption key can be changed. For sensitive data, the Crypto block is used.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| address | The address that gets encrypted is a masked 16-byte block address. The 32-bit address with the last 4 bits masked is placed as the last 4 bytes in the 128-bit input. The rest of the higher bit for the 128 bits are padded zeros by default. PA[127:0]: PA[3:0] = 0 PA[7:4] = ADDR[7:4]. PA[15:8] = ADDR[15:8]. PA[23:16] = ADDR[23:16]. PA[31:24] = ADDR[31:24]. The other twelve of the sixteen plain text address bytes of PA[127:0] are "0" by default. User can initialize PA[127:32] with Cy_SMIF_SetCryptoIV(). |
| data | This is the location where the input data-array is passed while the function is called. This array gets populated with the result after encryption is completed. |
| size | Provides a size of the array. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
| __STATIC_INLINE bool Cy_SMIF_BusyCheck | ( | SMIF_Type const * | base | ) |
This function provides the status of the IP block (False - not busy, True - busy).
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| __STATIC_INLINE void Cy_SMIF_Interrupt | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_stc_smif_context_t * | context | ||
| ) |
The Interrupt Service Routine for the SMIF.
The interrupt code will be responsible for the FIFO operations on FIFO interrupts during ongoing transfers. The user must place a call to this interrupt function in the interrupt routine corresponding to the interrupt attached to the SMIF. If the user does not do this, will break: the functionality of all the API functions in the SMIF driver that use SMIF interrupts to affect transfers.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| context | Passes a configuration structure that contains the transfer parameters of the SMIF block. |
All the Global variables described above are used when the Software Buffer is used.
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_CacheEnable | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_cache_t | cacheType | ||
| ) |
This function is used to enable the fast cache, the slow cache or both.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| cacheType | Holds the type of the cache to be modified. cy_en_smif_cache_t |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_CacheDisable | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_cache_t | cacheType | ||
| ) |
This function is used to disable the fast cache, the slow cache or both.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| cacheType | Holds the type of the cache to be modified. cy_en_smif_cache_t |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_CachePrefetchingEnable | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_cache_t | cacheType | ||
| ) |
This function is used to enable pre-fetching for the fast cache, the slow cache or both.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| cacheType | Holds the type of the cache to be modified. cy_en_smif_cache_t |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_CachePrefetchingDisable | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_cache_t | cacheType | ||
| ) |
This function is used to disable pre-fetching for the fast cache, the slow cache or both.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| cacheType | Holds the type of the cache to be modified. cy_en_smif_cache_t |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_CacheInvalidate | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_cache_t | cacheType | ||
| ) |
This function is used to invalidate/clear the fast cache, the slow cache or both.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| cacheType | Holds the type of the cache to be modified. cy_en_smif_cache_t |
| void Cy_SMIF_SetCryptoKey | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint32_t * | key | ||
| ) |
Sets the AES-128 encryption key into SMIF crypto registers.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| key | An array containing 128 bit crypto key: uint32_t key[4]. The least significant word first. |
| void Cy_SMIF_SetCryptoIV | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint32_t * | nonce | ||
| ) |
Sets the 96 bit initialization vector (nonce) into SMIF crypto registers.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| nonce | An array containing 96 bit initialization vector (nonce) |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_SetCryptoEnable | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_slave_select_t | slaveId | ||
| ) |
Enables SMIF encryption.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| slaveId | salve select line to indicate the device on which encryption should be enabled. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_SetCryptoDisable | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_slave_select_t | slaveId | ||
| ) |
Disables SMIF encryption.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| slaveId | salve select line to indicate the device on which encryption should be disabled. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_IsCryptoEnabled | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_slave_select_t | slaveId, | ||
| bool * | crypto_status | ||
| ) |
Checks the status of encryption for the selected slave device.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| slaveId | salve select line to indicate the device on which encryption should be disabled. |
| crypto_status | Holds the status of encryption. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_ConvertSlaveSlotToIndex | ( | cy_en_smif_slave_select_t | ss, |
| uint32_t * | device_idx | ||
| ) |
Converts Slave Select enum to the device index.
| ss | Slave Select enum. |
| device_idx | A pointer to device index to be returned. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_SetRxCaptureMode | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| cy_en_smif_capture_mode_t | mode, | ||
| cy_en_smif_slave_select_t | slaveId | ||
| ) |
This function sets the Rx Capture mode setting for SMIF IP block instance.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| mode | Rx Capture mode cy_en_smif_capture_mode_t |
| slaveId | Slave ID for which RX Capture configuration has to be updated. |
| bool Cy_SMIF_IsBridgeOn | ( | SMIF_Base_Type * | base | ) |
This function is used to check the bridge enable state.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF base registers. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_Bridge_Enable | ( | SMIF_Base_Type * | base, |
| bool | enable | ||
| ) |
This function is used to enable/disable Bridge.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF base registers. |
| enable | enable/disable the bridge |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_SetMasterDLP | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint16 | dlp, | ||
| uint8_t | size | ||
| ) |
This function sets the data learning pattern.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| dlp | data learning pattern (maximum 16-bit) |
| size | pattern size (allowed range 1 to 16 bits) |
| uint16_t Cy_SMIF_GetMasterDLP | ( | SMIF_Type * | base | ) |
This function gets the data learning pattern configured.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| uint8_t Cy_SMIF_GetMasterDLPSize | ( | SMIF_Type * | base | ) |
This function gets the data learning pattern size configured.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| uint8_t Cy_SMIF_GetTapNumCapturedCorrectDLP | ( | SMIF_Type * | base, |
| uint8_t | bit | ||
| ) |
This function gets number of delay taps used for specified data line.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block registers. |
| bit | DLP Tap selection for the bit position mapped as per Cy_SMIF_SetDataSelect. |
| uint32_t CY_SMIF_GetDelayTapsNumber | ( | volatile void * | base | ) |
This function returns tap number which the SMIF IP has.
User can input both SMIF DEVICE block address and SMIF block address
| base | Base address of the SMIF block or the SMIF DEVICE block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_InitCache | ( | SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type * | base, |
| const cy_stc_smif_cache_config_t * | cache_config | ||
| ) |
This function initializes SMIF internal CACHE with user provided configuration cy_stc_smif_cache_config_t.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block. |
| cache_config | Contains the configuration information to configure SMIF internal Cache. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_Clean_All_Cache | ( | SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type * | base | ) |
This function cleans complete SMIF internal CACHE.
This is a blocking call and returns with the status of CACHE clean operation.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_Invalidate_All_Cache | ( | SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type * | base | ) |
This function invalidates complete SMIF internal CACHE.
This is a blocking call and returns with the status of CACHE invalidate operation.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_Clean_And_Invalidate_All_Cache | ( | SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type * | base | ) |
This function cleans and invalidates complete SMIF internal CACHE.
This is a blocking call and returns with the status of CACHE invalidate and clean operation.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_Clean_Cache_by_Addr | ( | SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type * | base, |
| bool | is_secure_view, | ||
| uint32_t | address, | ||
| uint32_t | size | ||
| ) |
This function cleans cache using the address and size specified by user.
This is a blocking call and returns with the status of CACHE clean operation. Size must be specified in multiples of CACHE line size (32 bytes).
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block. |
| is_secure_view | Specifies the view on which cache operation has to be performed. In non-secure world this parameter is ignored and defaulted to non-secure view cache operation. |
| address | start address from which cache operation should be performed. |
| size | size in multiples of CACHE line size CY_SMIF_CACHE_LINE_SIZE_IN_BYTES. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_Invalidate_Cache_by_Addr | ( | SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type * | base, |
| bool | is_secure_view, | ||
| uint32_t | address, | ||
| uint32_t | size | ||
| ) |
This function invalidates cache using the address and size specified by user.
This is a blocking call and returns with the status of CACHE invalidate operation. Size must be specified in multiples of CACHE line size (32 bytes).
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block. |
| is_secure_view | Specifies the view on which cache operation has to be performed. In non-secure world this parameter is ignored and defaulted to non-secure view cache operation. |
| address | start address from which cache operation should be performed. |
| size | size in multiples of CACHE line size CY_SMIF_CACHE_LINE_SIZE_IN_BYTES. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_Clean_And_Invalidate_Cache_by_Addr | ( | SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type * | base, |
| bool | is_secure_view, | ||
| uint32_t | address, | ||
| uint32_t | size | ||
| ) |
This function cleans and invalidates cache using the address and size specified by user.
This is a blocking call and returns with the status of CACHE operation. Size must be specified in multiples of CACHE line size (32 bytes).
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block. |
| is_secure_view | Specifies the view on which cache operation has to be performed. In non-secure world this parameter is ignored and defaulted to non-secure view cache operation. |
| address | start address from which cache operation should be performed. |
| size | size in multiples of CACHE line size CY_SMIF_CACHE_LINE_SIZE_IN_BYTES. |
| cy_en_smif_status_t Cy_SMIF_IsCacheEnabled | ( | SMIF_CACHE_BLOCK_Type * | base, |
| bool * | cache_status | ||
| ) |
This function checks whether Cache is enabled or not.
| base | Holds the base address of the SMIF block. |
| cache_status | Holds the Cache status |