This driver provides the user an easy method for accessing standard Host Controller Interface (HCI) registers and provides some simple functionality on top of the HCI for reading and writing data to an SD card, eMMc card or a SDIO device.
The functions and other declarations used in this driver are in cy_sd_host.h. You can include cy_pdl.h to get access to all functions and declarations in the PDL.
Features:
- Supports data transfer using CPU, SDMA, ADMA2 and ADMA3 modes
- Supports a configurable block size (1 to 65,535 Bytes)
- Supports interrupt enabling and masking
- Supports SD-HCI Host version 4 mode or less
- Compliant with the SD 6.0, SDIO 4.10 and eMMC 5.1 specifications and earlier versions
- SD interface features:
- - Supports the 4-bit interface
- - Supports Ultra High Speed (UHS-I) mode
- - Supports Default Speed (DS), High Speed (HS), SDR12, SDR25, SDR50, and DDR50 speed modes
- - Supports SDIO card interrupts in both 1-bit and 4-bit modes
- - Supports Standard capacity (SDSC), High capacity (SDHC) and Extended capacity (SDXC) memory
- - Supports CRC and check for command and data packets
- - Supports packet timeouts
- - Handles the SDIO card interrupt
- eMMC interface features:
- - Supports 1-bit/4-bit/8-bit interfaces
- - Supports legacy and High Speed SDR speed modes
- - Supports CRC and check for command and data packets
- - Supports packet timeouts
Unsupported Features:
- Wrap address transfers
- eMMC boot operation
- Suspend/Resume operation in an SDIO card
- Operation in SDR104, UHS-II mode, HS200, and HS400
- Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) protocol mode
- Interrupt input pins for the embedded SD system
- Auto-tuning
- Command queuing
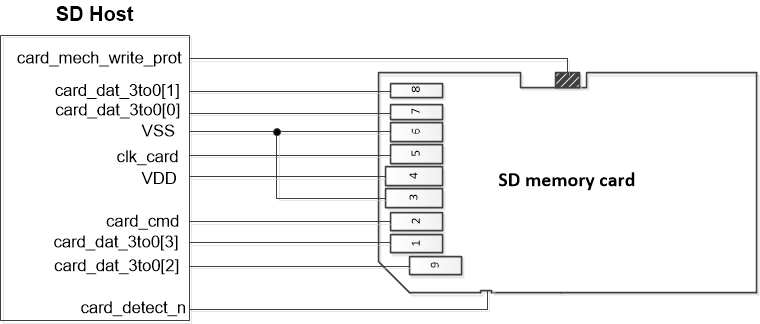
The SD, eMMC, and SDIO cards have the similar physical interface: clock, command line, and data lines. The SD card is removable and requires the SD card connector to connect to the PSoC device. This connector also has the card_mech_write_prot switch for mechanical write protection and the card_detect_n switch for card detection. The eMMC card also has DAT4-DAT7 pins for 8-bit mode and the EMMC_RESET pin.
The driver has a low-level and high-level APIs. The low-level functions provide an easy method to read and write registers. Also, these functions allow valid interaction with an SD Card, eMMC card, and SDIO card. The high-level functions provide an easy mechanism to enumerate a device, read, write, and erase data. They are RTOS-friendly. When starting a command, these functions do not wait until the command completes. The interrupt and flags are used to check when the transfer completes. This allows to put RTOS delays in the user code.
Configuration Considerations
The SD Host driver configuration can be divided to a number of sequential steps listed below:
- Note
- The SD Host driver is built on top of the SDHC hardware block. The SDHC1 instance is used as an example for all code snippets. Modify the code to match your design.
Enable SD Host
Enable the SDHC block calling Cy_SD_Host_Enable.
Assign and Configure Pins
Only dedicated SD Host pins can be used for SD Host operation. The HSIOM register must be configured to connect the block to the pins. Also, the SD Host pins must be configured in Strong Drive, Input buffer on:
#define SDHC1_PORT1 (P12_0_PORT)
#define SDHC1_PORT2 (P13_0_PORT)
#define SDHC1_IO_VOLT_SEL_NUM (P12_7_NUM)
#define SDHC1_CARD_DETECT_N_NUM (P12_1_NUM)
#define SDHC1_CARD_MECH_WRITE_PROT_NUM (P12_2_NUM)
#define SDHC1_LED_CTRL_NUM (P12_3_NUM)
#define SDHC1_CARD_IF_PWR_EN_NUM (P12_6_NUM)
#define SDHC1_CARD_EMMC_RESET_N_NUM (P12_0_NUM)
#define SDHC1_CARD_CMD_NUM (P12_4_NUM)
#define SDHC1_CLK_CARD_NUM (P12_5_NUM)
#define SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO00_NUM (P13_0_NUM)
#define SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO01_NUM (P13_1_NUM)
#define SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO02_NUM (P13_2_NUM)
#define SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO03_NUM (P13_3_NUM)
Cy_GPIO_SetHSIOM(SDHC1_PORT1, SDHC1_CARD_DETECT_N_NUM, P12_1_SDHC1_CARD_DETECT_N);
Cy_GPIO_SetHSIOM(SDHC1_PORT1, SDHC1_CARD_MECH_WRITE_PROT_NUM, P12_2_SDHC1_CARD_MECH_WRITE_PROT);
Cy_GPIO_SetHSIOM(SDHC1_PORT1, SDHC1_CARD_IF_PWR_EN_NUM, P12_6_SDHC1_CARD_IF_PWR_EN);
Cy_GPIO_SetHSIOM(SDHC1_PORT1, SDHC1_CARD_EMMC_RESET_N_NUM, P12_0_SDHC1_CARD_EMMC_RESET_N);
Cy_GPIO_SetHSIOM(SDHC1_PORT2, SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO00_NUM, P13_0_SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO00);
Cy_GPIO_SetHSIOM(SDHC1_PORT2, SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO01_NUM, P13_1_SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO01);
Cy_GPIO_SetHSIOM(SDHC1_PORT2, SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO02_NUM, P13_2_SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO02);
Cy_GPIO_SetHSIOM(SDHC1_PORT2, SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO03_NUM, P13_3_SDHC1_CARD_DAT_3TO03);
#define CY_GPIO_DM_STRONG
Strong Drive.
Definition: cy_gpio.h:522
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_GPIO_SetDrivemode(GPIO_PRT_Type *base, uint32_t pinNum, uint32_t value)
Configures the pin output buffer drive mode and input buffer enable.
Definition: cy_gpio.h:1286
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_GPIO_SetHSIOM(GPIO_PRT_Type *base, uint32_t pinNum, en_hsiom_sel_t value)
Configures the HSIOM connection to the pin.
Definition: cy_gpio.h:925
Assign Clock Source
The SD Host is sourced from the CLK_HF clock. The clock must be set to 100 MHz:
@ CY_SYSCLK_CLKHF_IN_CLKPATH0
clkHf input is Clock Path 0
Definition: cy_sysclk.h:2527
@ CY_SYSCLK_CLKHF_NO_DIVIDE
don't divide clkHf
Definition: cy_sysclk.h:2559
cy_en_sysclk_status_t Cy_SysClk_ClkHfSetSource(uint32_t clkHf, cy_en_clkhf_in_sources_t source)
Selects the source of the selected clkHf.
Definition: cy_sysclk_v2.c:3244
cy_en_sysclk_status_t Cy_SysClk_ClkHfSetDivider(uint32_t clkHf, cy_en_clkhf_dividers_t divider)
Sets the pre-divider for a clkHf.
Definition: cy_sysclk_v2.c:3263
cy_en_sysclk_status_t Cy_SysClk_ClkHfEnable(uint32_t clkHf)
Enables the selected clkHf.
Definition: cy_sysclk_v2.c:3169
Configure Interrupt (Optional)
The user can set up the interrupt for SD Host operation. The user is responsible for writing its own Interrupt handler. The Interrupt must be called in the interrupt handler for the selected SDHC instance. Also this interrupt must be enabled in the NVIC otherwise it will not work. It is the user's responsibility to clear the normal and error interrupt statuses. The interrupt statuses can be read using Cy_SD_Host_GetNormalInterruptStatus and Cy_SD_Host_GetErrorInterruptStatus. To clear the interrupt statuses, use Cy_SD_Host_ClearNormalInterruptStatus and Cy_SD_Host_ClearErrorInterruptStatus.
void SD_Host_User_Isr(void)
{
uint32_t normalStatus;
uint32_t errorStatus;
if (0u < normalStatus)
{
}
if (0u < errorStatus)
{
}
}
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_SD_Host_ClearErrorInterruptStatus(SDHC_Type *base, uint32_t status)
Clears the error interrupt status.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:2031
__STATIC_INLINE uint32_t Cy_SD_Host_GetErrorInterruptStatus(SDHC_Type const *base)
Returns the error Int Status register.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:2008
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_SD_Host_ClearNormalInterruptStatus(SDHC_Type *base, uint32_t status)
Clears the selected SD host normal status.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1905
__STATIC_INLINE uint32_t Cy_SD_Host_GetNormalInterruptStatus(SDHC_Type const *base)
Returns the normal Int Status register.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1882
#define SD_Host_INTR_NUM sdhc_1_interrupt_general_IRQn
#define SD_Host_INTR_PRIORITY (3UL)
{
#if (CY_CPU_CORTEX_M0P)
NvicMux4_IRQn,
SD_Host_INTR_NUM,
#else
SD_Host_INTR_NUM,
#endif
SD_Host_INTR_PRIORITY
};
__enable_irq();
#if (CY_CPU_CORTEX_M0P)
NVIC_EnableIRQ(NvicMux4_IRQn);
#else
NVIC_EnableIRQ(SD_Host_INTR_NUM);
#endif
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_SD_Host_SetNormalInterruptMask(SDHC_Type *base, uint32_t interruptMask)
Setting a bit in this register allows the enabled status to cause an interrupt.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1966
#define CY_SD_HOST_CARD_INSERTION
Card insertion.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:764
#define CY_SD_HOST_CARD_REMOVAL
Card removal.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:771
Initialization configuration structure for a single interrupt channel.
Definition: cy_sysint.h:227
cy_en_sysint_status_t Cy_SysInt_Init(const cy_stc_sysint_t *config, cy_israddress userIsr)
Initializes the referenced interrupt by setting the priority and the interrupt vector.
Definition: cy_sysint_v2.c:80
Configure SD Host
To set up the SD Host driver, provide the configuration parameters in the cy_stc_sd_host_init_config_t structure. Set the emmc parameter to true for the eMMC-device, otherwise set it to false. Set dmaType if DMA mode is used for read/write operations. The other parameters are optional for operation. To initialize the driver, call the Cy_SD_Host_Init function providing a pointer to the filled cy_stc_sd_host_init_config_t structure and allocated cy_stc_sd_host_context_t.
Context structure.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1401
{
.enableLedControl = false,
.emmc = false,
};
cy_en_sd_host_dma_type_t dmaType
Selects the DMA type to be used.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1337
SD Host initialization configuration structure.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1335
@ CY_SD_HOST_DMA_ADMA2
ADMA2 mode.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1280
cy_en_sd_host_status_t Cy_SD_Host_Init(SDHC_Type *base, const cy_stc_sd_host_init_config_t *config, cy_stc_sd_host_context_t *context)
Initializes the SD host module.
Definition: cy_sd_host.c:2950
The SD, eMMC or SDIO card can be configured using the Cy_SD_Host_InitCard function as a pointer to the filled cy_stc_sd_host_sd_card_config_t structure and allocated cy_stc_sd_host_context_t.
Initialize the card
Finally, enable the card operation calling Cy_SD_Host_InitCard.
uint32_t rca;
{
.cardType = &cardType,
.rca = &rca,
.cardCapacity = &cardCapacity,
};
bool lowVoltageSignaling
If true, the host supports the 1.8V signaling.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1347
SD/eMMC card configuration structure.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1346
cy_en_sd_host_card_type_t
Card type.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1247
cy_en_sd_host_card_capacity_t
The card capacity type.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1258
@ CY_SD_HOST_BUS_WIDTH_4_BIT
The 4-bit mode data transfer width.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1191
cy_en_sd_host_status_t Cy_SD_Host_InitCard(SDHC_Type *base, cy_stc_sd_host_sd_card_config_t *config, cy_stc_sd_host_context_t *context)
Initializes a card if it is connected.
Definition: cy_sd_host.c:653
Common Use Cases
SD card Operation
The master API is divided into two categories: High-Level and Low-Level. Therefore, there are two methods for initiating SD card transactions using either Low-Level or High-Level API.
Use High-Level Functions
Call Cy_SD_Host_Read or Cy_SD_Host_Write to communicate with the SD memory device. These functions do not block in DMA mode and only start a transaction. After a transaction starts, the user should check the further data-transaction complete event. The example below shows sending and reading data in DMA mode.
#define DATA (7U)
memset(txBuff, DATA, sizeof(txBuff));
data.
data = (uint32_t*)txBuff;
{
{
}
}
data.
data = (uint32_t*)rxBuff;
{
{
}
}
uint32_t dataTimeout
The timeout value for the transfer.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1394
bool enReliableWrite
For EMMC cards, enables the reliable write.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1395
bool enableDma
Enables DMA for the transaction.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1396
uint32_t address
The address to Write/Read data on the card or eMMC.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1391
cy_en_sd_host_auto_cmd_t autoCommand
Selects which auto commands are used if any.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1393
uint32_t * data
The pointer to data.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1390
uint32_t numberOfBlocks
The number of blocks to Write/Read.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1392
SD Host Write/Read structure.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1389
cy_en_sd_host_status_t
SD host error codes.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1175
@ CY_SD_HOST_AUTO_CMD_NONE
Auto command disable.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1132
@ CY_SD_HOST_SUCCESS
Successful.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1176
cy_en_sd_host_status_t Cy_SD_Host_Read(SDHC_Type *base, cy_stc_sd_host_write_read_config_t *config, cy_stc_sd_host_context_t const *context)
Reads single- or multiple-block data from the SD card / eMMC.
Definition: cy_sd_host.c:917
cy_en_sd_host_status_t Cy_SD_Host_Write(SDHC_Type *base, cy_stc_sd_host_write_read_config_t *config, cy_stc_sd_host_context_t const *context)
Writes single- or multiple-block data to the SD card / eMMC.
Definition: cy_sd_host.c:1066
#define CY_SD_HOST_XFER_COMPLETE
Transfer complete.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:727
#define CY_SD_HOST_BLOCK_SIZE
The SD memory card block size.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:345
Use Low-Level Functions
Call Cy_SD_Host_InitDataTransfer to initialize the SD block for a data transfer. It does not start a transfer. To start a transfer call Cy_SD_Host_SendCommand after calling this function. If DMA is not used for Data transfer then the buffer needs to be filled with data first if this is a write. Wait the transfer complete event. ADMA3 mode requires calling Cy_SD_Host_InitDataTransfer to initialize the DMA transaction. The ADMA3 mode example is shown below.
#define WR_BLOCK_NUM (2UL)
#define RD_BLOCK_NUM (4UL)
#define VALUE1 (0x1U)
#define VALUE2 (0x3U)
uint32_t integratedDescriptor[6];
uint32_t cmdDescriptor0[10];
uint32_t cmdDescriptor1[10];
uint32_t cmdDescriptor2[10];
uint32_t wrRdAddress = 0UL;
uint32_t wrAddress2 = WR_BLOCK_NUM;
memset(txBuff_1, VALUE1, sizeof(txBuff_1));
memset(txBuff_2, VALUE2, sizeof(txBuff_2));
memset(rxBuff, 0UL, sizeof(rxBuff));
{
}
dataConfig.
data = (uint32_t*)&integratedDescriptor[0];
memset(integratedDescriptor, 0UL, sizeof(integratedDescriptor));
memset(cmdDescriptor0, 0UL, sizeof(cmdDescriptor0));
memset(cmdDescriptor1, 0UL, sizeof(cmdDescriptor1));
memset(cmdDescriptor2, 0UL, sizeof(cmdDescriptor2));
integratedDescriptor[1] = (uint32_t)&cmdDescriptor0[0];
integratedDescriptor[3] = (uint32_t)&cmdDescriptor1[0];
integratedDescriptor[5] = (uint32_t)&cmdDescriptor2[0];
cmdDescriptor0[1] = WR_BLOCK_NUM;
cmdDescriptor0[5] = wrRdAddress;
cmdDescriptor0[7] = 25UL << (16U + 0x8U) |
1UL << (16U + 0x5U) |
1UL << (16U + 0x4U) |
1UL << (16U + 0x3U) |
1UL << (0x5U) |
0UL << (0x4U) |
1UL << (0x1U) |
1UL << (0x0U) |
1UL << (0x8U);
cmdDescriptor0[9] = (uint32_t)&txBuff_1;
cmdDescriptor1[1] = WR_BLOCK_NUM;
cmdDescriptor1[5] = wrAddress2;
cmdDescriptor1[7] = 25UL << (16U + 0x8U) |
1UL << (16U + 0x5U) |
1UL << (16U + 0x4U) |
1UL << (16U + 0x3U) |
1UL << (0x5U) |
0UL << (0x4U) |
1UL << (0x1U) |
1UL << (0x0U) |
1UL << (0x8U);
cmdDescriptor1[9] = (uint32_t)&txBuff_2;
cmdDescriptor2[1] = RD_BLOCK_NUM;
cmdDescriptor2[5] = wrRdAddress;
cmdDescriptor2[7] = 18UL << (16U + 0x8U) |
1UL << (16U + 0x5U) |
1UL << (16U + 0x4U) |
1UL << (16U + 0x3U) |
1UL << (0x5U) |
1UL << (0x4U) |
1UL << (0x1U) |
1UL << (0x0U) |
1UL << (0x8U);
cmdDescriptor2[9] = (uint32_t)&rxBuff;
{
{
}
}
uint32_t * data
The pointer to data to send/receive or the pointer to the DMA descriptor.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1379
bool enableDma
Enables DMA for the transaction.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1376
cy_en_sd_host_card_capacity_t cardCapacity
The standard card or the card with the high capacity.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1403
The SD Host data transfer configuration structure.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1373
@ CY_SD_HOST_AUTO_CMD_12
Auto command 12 enable.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1133
@ CY_SD_HOST_RESPONSE_LEN_48
Response Length 48.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1272
@ CY_SD_HOST_SDSC
SDSC - Secure Digital Standard Capacity (up to 2 GB).
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:1259
cy_en_sd_host_status_t Cy_SD_Host_InitDataTransfer(SDHC_Type *base, cy_stc_sd_host_data_config_t const *dataConfig)
Initializes the SD block for a data transfer.
Definition: cy_sd_host.c:5051
#define CY_SD_HOST_SDSC_ADDR_SHIFT
This constant is used to get the address for the SDSC card using the shift operation instead of multi...
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:347
#define CY_SD_HOST_ADMA_TRAN
Transfers data of one descriptor line.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:376
#define CY_SD_HOST_ADMA_ATTR_END_POS
The ADMA Attr End position.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:384
#define CY_SD_HOST_ADMA_ATTR_VALID_POS
The ADMA Attr Valid position.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:383
#define CY_SD_HOST_ADMA_LEN_POS
The ADMA Len position.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:388
#define CY_SD_HOST_ADMA3_CMD
The Command descriptor.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:378
#define CY_SD_HOST_ADMA3_INTEGRATED
The Integrated descriptor.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:379
#define CY_SD_HOST_ADMA_ATTR_INT_POS
The ADMA Attr Int position.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:385
#define CY_SD_HOST_ADMA_ACT_POS
The ADMA Act position.
Definition: cy_sd_host.h:386
eMMC Card Operation
eMMC cards use the same API for writing and reading data. Additionally, eMMC requires configuring GPIO pins for DAT signals in 8-bit mode and card_emmc_reset_n pin if needed. The emmc member of cy_stc_sd_host_init_config_t structure must be set to "true".
eMMC SDIO or Combo Card Operation
Cy_SD_Host_InitCard() initializes all types of cards and automatically detects the card type: SD, SDIO or Combo card. SDIO cards have their input-output (I/O) functions that can be controlled using the GPIO driver. Combo Cards can use both I/O and memory API.
Low Power Support
The SD Host does not operate in Hibernate and Deep Sleep modes but it can automatically continue write/read operation after restoring from Deep Sleep mode. SD CLK must be disabled before going to Deep Sleep mode and can be enabled after wake up from Deep Sleep mode. To reduce the power consumption in Active mode, the user can stop the clock of the SD bus but the following interrupts can be allowed: Card Insert, Card Removal and SDIO Interrupt.
SD Card Removal and Insertion
SD card removal or insertion can be detected by calling Cy_SD_Host_GetNormalInterruptStatus which returns the card removal or card insertion events (CY_SD_HOST_CARD_REMOVAL or CY_SD_HOST_CARD_INSERTION bits). These events should be reset using Cy_SD_Host_ClearNormalInterruptStatus when they occur. When the card is removed, the SDHC block disables the CMD/DAT output. It is recommended to set DAT pins to the Digital High-Z (CY_GPIO_DM_HIGHZ) drive mode when card removal is detected. This can be doing using the GPIO driver. When the card is inserted, the SDHC block automatically disables the card power and clock. After card insertion, the user should set the DAT pins drive mode back to Strong Drive, Input buffer on (CY_GPIO_DM_STRONG), and then call Cy_SD_Host_InitCard.
- Note
- If CARD_INTERRUPT is enabled and DAT pins are not set to Digital High-Z drive mode then the interrupt will continuously trigger because the DAT1 line is driven low upon card re-insertion. The user will have to detect the card removal in the ISR handler, apply the power to the card using Cy_SD_Host_EnableCardVoltage, set to the DAT pins drive mode to the Digital High-Z (CY_GPIO_DM_HIGHZ) and clear CY_SD_HOST_CARD_INTERRUPT bit using Cy_SD_Host_ClearNormalInterruptStatus.
Low Voltage Signaling
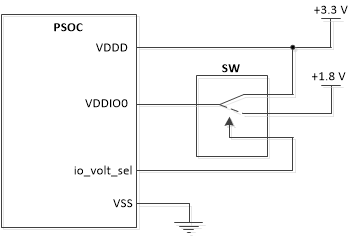
When lowVoltageSignaling is true, the SD Host driver sets UHS-I mode during the card initialization. The SD Host driver always starts talking to the card at 3.3V and then later switches to 1.8V. There is no internal regulator in the PSoC 6 to change SD signals from 3.3V to 1.8V. Thus, an external regulator is needed for the VDDIO of the PSoC device to provide the ability to go from 3.3V to 1.8V. The SD Host driver sets the io_volt_sel pin to high which is used to control the external regulator.
More Information
Refer to the appropriate device technical reference manual (TRM) for a detailed description of the registers.