The RadarSensing Library provides a high-level interface for multiple radar use cases. RADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging) is a device that uses electromagnetic waves to obtain range, angle or velocity of targets. Radar systems are used in a number of areas covering a variety of applications. Some of them include (but not limited to):
There are a number of reasons behind the use of radar in the aforementioned applications:
A typical radar system consists of the following components:
This is represented by the following figure:
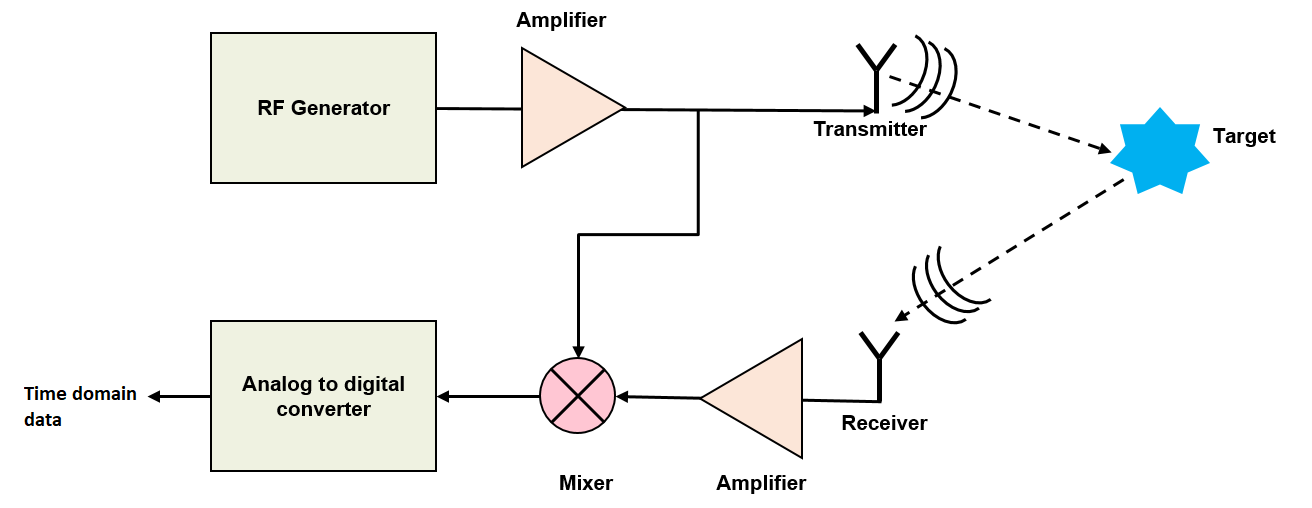
An electromagnetic wave generated by the RF generator is amplified and then transmitted through the transmitter. The wave travels at a constant speed, approximately at the speed of light and gets reflected once it strikes a target. The reflected signal is collected by the receiver, amplified and fed to a mixer where it gets mixed with the transmitted signal. The resulting signal from the mixer is called as IF (Intermediate frequency) signal, whose instantaneous frequency is equal to the difference of the instantaneous frequencies of the two input signals and phase is equal to the phase difference of the two input signals. The IF signal is digitized through an ADC, resulting in a time domain data which can then be processed further for different use cases.
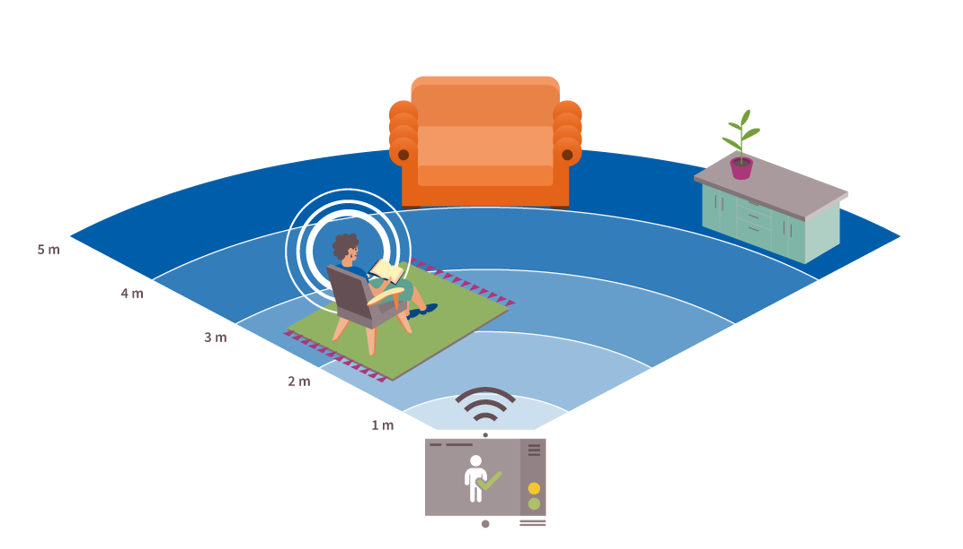
This application detects human presence within a configurable distance and a certain field of view from the radar. The maximum range to detect human presence can be configured using RadarSensing libary API. Presence detection can be further utilized for applications such as keyword-less authentication, automatic user interaction with smart devices and many more. The following figure shows a high-level representation of presence detection:
This application counts the number of people entering and exiting a location such as an office building, cafeteria, supermarket etc. This allows customers to determine the occupancy of their premises, thus enabling various solutions such as maintaining social distancing, evacuating in case of an emergency and saving energy based on occupancy. Furthermore, the entrance counter data can be sent to a centralized server and remotely displayed on laptops or mobile devices to understand the occupancy level. The following figure shows a high-level representation of entrance counter:

The above use cases are implemented using Infineon's XENSIV™ 60GHz radar: https://www.infineon.com/cms/en/product/sensor/radar-sensors/radar-sensors-for-iot/60ghz-radar/