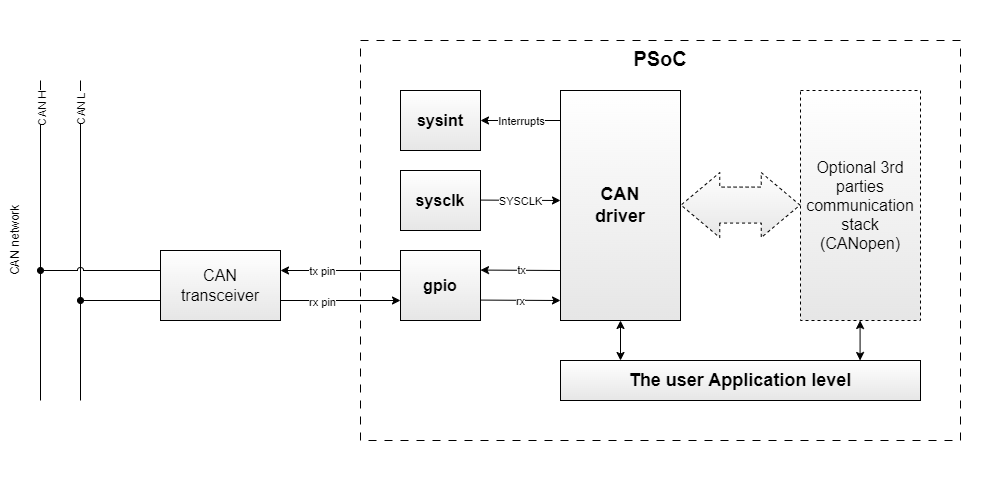
The CAN driver provides an easy method to access the CAN IP block registers and provides simple functionality for sending and receiving data between devices in the CAN network. More...
Modules | |
| Macros | |
| This section describes the CAN Macros. | |
| Functions | |
| Data Structures | |
| Enumerated Types | |
The CAN driver provides an easy method to access the CAN IP block registers and provides simple functionality for sending and receiving data between devices in the CAN network.
The CAN driver provides an API to configure the main features - bit time, message buffers - and transmit and receive the CAN message. The CAN driver is not compatible with CAN FD or future versions.
Specification of the sample code is as follows:
The steps to generate initialization code using the ModusToolbox Device Configurator Tool:
Now, all required CAN initialization code and configuration prerequisites will be generated:
For the CAN interrupt service routine, Cy_CAN_IrqHandler() can be used. It handles reading data from Rx buffers. Corresponding callback functions are called for error interrupts, Rx interrupts and Tx complete interrupt. Put the names of callback functions to the Callback functions parameters section. Put NULL if no callback function to be used.
Set up the interrupt handler to be called with CAN events. The following code shows how to set up the interrupt handler:
Call Cy_CAN_Init() to initialize the CAN module. It initializes the CAN module with the configuration parameters, passed in the cy_stc_can_config_t structure. It consists of several elements to be defined first.
The Cy_CAN_Init() function also initializes the shared context structure used later with other API functions.
Although the callback functions are optional, they are recommended for use, otherwise, there is no report to the API about any error and transmission or reception events. The example callback function sends received data back to the bus, incrementing ID by 1:
The CAN block uses the Port 4 or 6 pins for receive (P4[0],P6[1]) and transmit (P4[1],P6[2]).
For the CAN interrupt service routine, the Cy_CAN_IrqHandler() can be used. It handles reading data from Rx buffers. Corresponding callback functions are called for error interrupts, Rx interrupts and Tx complete interrupt.
Setup the interrupt handler to be called with the CAN events. The following code shows how to set up the interrupt handler:
The CAN has a bit rate setting. It consists of a pre-scaler, time segment 1, time segment 2 and synchronization jump width.
The CAN time quantum (tq) may be programmed in the range of 1 to 32768 CAN clock periods: tq = (prescaler + 1) * Tsys, where Tsys is System Clock clock period. The length of the bit time is (programmed values) [timeSegment1 + timeSegment2 + 3] tq. The example below shows the configuration with the 250 kbps bit rate. This assumes the SYSCLK frequency of 48 MHz for the CAN block.
CAN driver provides API to setup Message ID filtering. One filter can be set for one Rx buffer. The desired count of the filters(buffers) is specified in the cy_stc_can_config_t structure and is set once during block initialization. It is possible to change the configured filter setting with Cy_CAN_UpdateRxBufferConfig().
The cy_stc_can_config_t structure is used to pass all configuration to Cy_CAN_Init() function. It is populated with pointers to other structures required and constants, defined before.
The Cy_CAN_Init() function initializes the CAN block by writing CAN configuration registers. Cy_CAN_Init() enables the Rx interrupts for new message reception into the Rx buffers. Cy_CAN_Init() also enables the Tx interrupts for the Tx buffers successful transmission. The code example also shows the test mode configuration which can be used to enable the internal loopback mode. See cy_en_can_test_mode_t for details. Cy_CAN_Init() sets test mode configuration to CY_CAN_TEST_MODE_DISABLE. Remember to disable the echo functionality in the Rx callback when using a loopback.
To send a CAN message, a message structure must be prepared which consists of the CAN ID , data and data length.
To transmit CAN messages, the function Cy_CAN_Transmit() is used. The buffer status can be retrieved by Cy_CAN_GetTxBufferStatus(). It is possible to set a callback function which will be notified whenever a message transmission has been completed.
For more information on the CAN peripheral, refer to the technical reference manual (TRM).
| Version | Changes | Reason for Change |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | Initial version |