The System Clock (SysClk) driver contains the API for configuring system and peripheral clocks.
The functions and other declarations used in this driver are in cy_sysclk.h. You can include cy_pdl.h to get access to all functions and declarations in the PDL.
Firmware uses the API to configure, enable, or disable a clock.
The clock system includes a variety of resources that can vary per device, including:
Consult the Technical Reference Manual for your device for details of the clock system.
The PDL defines clock system capabilities in:
devices/include/<series>_config.h. (E.g. devices/include/pse84_config.h).
As an illustration of the clocking system, the following diagram shows the PSOC EDGE E8 clock tree. The actual tree may vary depending on the device series. Consult the Technical Reference Manual for your device for details.
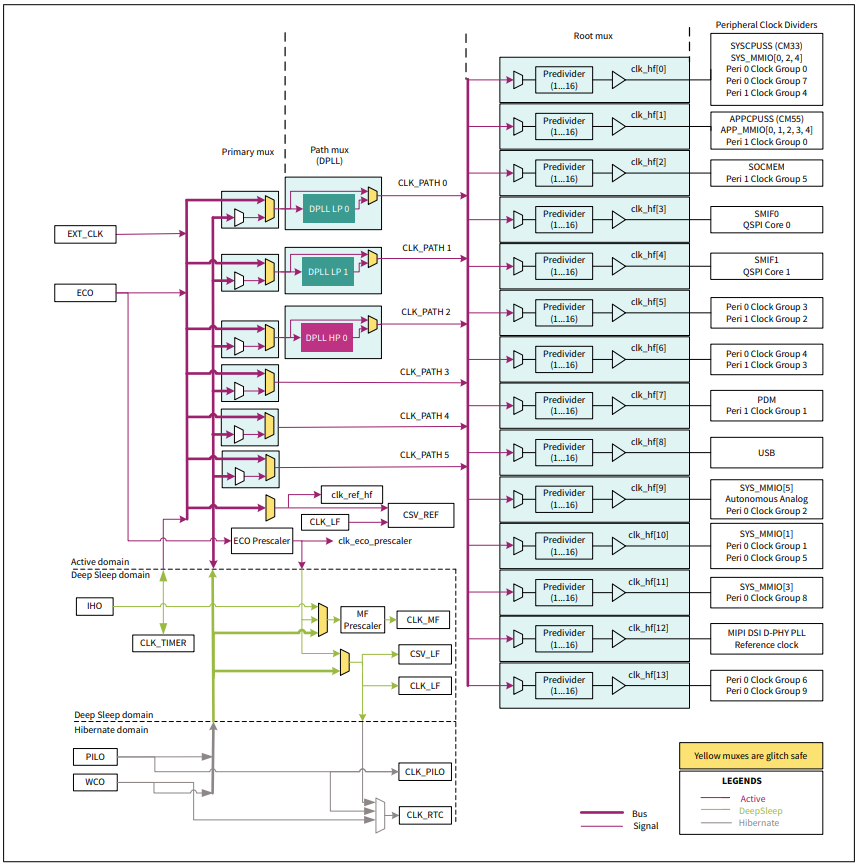
The availability of clock functions depend on the availability of the chip resources that support those functions. Consult the device TRM before attempting to use these functions.
Some SysCLK APIs are marked as Secure Aware. This means that if the clock hardware is marked as a secure resource in the Peripheral Protection Controller (PPC) and these APIs are called from a non-secure CPU state, the PDL will submit a request to the Secure Request Framework (SRF) middleware to transition to a secure CPU state to perform the operation. From the application's perspective, the API will behave the same whether it is called from a secure or non-secure CPU state albeit slower.
SysCLK requires that the clock trees are secured upwards. That is, if a peripheral clock divider is secured, then the HF clk that sources it must be secured, and then the CLK_PATH and so on. The inverse is not true. If a HF clk is secured, the peripheral clock divider can be either secured or non-secured. Similarly, if the peripheral clock divider is non-secured, then the HF clk can be either secured or non-secured.
This functionality is automatically enabled on devices with ARM TrustZone processors. To disable, set the DEFINE+=CY_PDL_ENABLE_SECURE_AWARE_SYSCLK=0 in the application Makefile.
For more information on Secure Aware PDL behavior, see Secure Aware PDL.
Refer to the technical reference manual (TRM) and the device datasheet.
API Reference | |
| Macros | |
| General Enumerated Types | |
| External Clock Source (EXTCLK) | |
| The External Clock Source (EXTCLK) is a clock source routed into SOC through a GPIO pin. | |
| External Crystal Oscillator (ECO) | |
| The External Crystal Oscillator (ECO) is a clock source that consists of an oscillator circuit that drives an external crystal through its dedicated ECO pins. | |
| Clock Path Source | |
| Clock paths are a series of multiplexers that allow a source clock to drive multiple clocking resources down the chain. | |
| Phase Locked Loop (PLL) | |
| The PLL is a clock generation circuit that can be used to produce a higher frequency clock from a reference clock. | |
| Precision Internal Low-Speed Oscillator (PILO) | |
| PILO provides a higher accuracy 32.768 kHz clock than the ILO. | |
| Clock Measurement | |
| These functions measure the frequency of a specified clock relative to a reference clock. | |
| Low Power Callback | |
| Entering and exiting low power modes require compatible clock configurations to be set before entering low power and restored upon wake-up and exit. | |
| Watch Crystal Oscillator (WCO) | |
| The WCO is a highly accurate 32.768 kHz clock source capable of operating in all power modes (excluding the Off mode). | |
| High-Frequency Clocks | |
| Multiple high frequency clocks (CLK_HF) are available in the device. | |
| Peripherals Clock Dividers | |
| There are multiple peripheral clock dividers that, in effect, create multiple separate peripheral clocks. | |
| Peripheral Group(MMIO Group) Controls | |
| All the peripherals in the SOC belongs to certain MMIO groups. | |
| Low-Frequency Clock | |
| The low-frequency clock is the source clock for the MCWDT (Multi-Counter Watchdog) and can be the source clock for Backup Domain Clock, which drives the RTC (Real-Time Clock). | |
| Backup Domain Clock | |
| The backup domain clock drives the RTC (Real-Time Clock). | |
| Internal High Frequency(IHO) Clock | |
| The IHO Clock is Internal High-speed Oscillator, which is present in CAT1B(48MHz) and PSE8(50MHz) devices. | |