Configures a DMA channel and its descriptor(s).
The functions and other declarations used in this driver are in cy_dma.h. You can include cy_pdl.h to get access to all functions and declarations in the PDL.
The DMA channel can be used in any project to transfer data without CPU intervention basing on a hardware trigger signal from another component.
A device may support more than one DMA hardware block. Each block has a set of registers, a base hardware address, and supports multiple channels. Many API functions for the DMA driver require a base hardware address and channel number. Ensure that you use the correct hardware address for the DMA block in use.
Features:
- Multiple DW blocks (device specific)
- Multiple channels per each DW block (device specific)
- Four priority levels for each channel
- Byte, half-word (2-byte), and word (4-byte) transfers
- Configurable source and destination addresses
- CRC calculation support (only for CPUSS_ver2)
Configuration Considerations
To set up a DMA driver, initialize a descriptor, initialize and enable a channel, and enable the DMA block.
To set up a descriptor, provide the configuration parameters for the descriptor in the cy_stc_dma_descriptor_config_t structure. Then call the Cy_DMA_Descriptor_Init function to initialize the descriptor in SRAM. You can modify the source and destination addresses dynamically by calling Cy_DMA_Descriptor_SetSrcAddress and Cy_DMA_Descriptor_SetDstAddress.
To set up a DMA channel, provide a filled cy_stc_dma_channel_config_t structure. Call the Cy_DMA_Channel_Init function, specifying the channel number. Use Cy_DMA_Channel_Enable to enable the configured DMA channel.
Call Cy_DMA_Channel_Enable for each DMA channel in use.
When configured, another peripheral typically triggers the DMA. The trigger is connected to the DMA using the trigger multiplexer. The trigger multiplexer driver has a software trigger you can use in firmware to trigger the DMA. See the Trigger Multiplexer documentation.
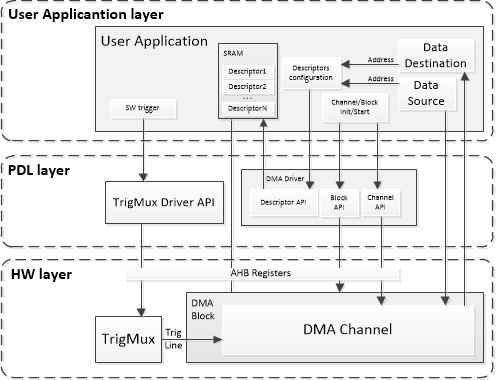
The following is a simplified structure of the DMA driver API interdependencies in a typical user application:
NOTE: DMA Trigger can also be provided through Cy_DMA_Channel_SetSWTrigger API on supported targets.
NOTE: DMA will read descriptors from SRAM memory. To run DMA on devices with Core CM7, D cache needs to be cleaned before DMA transfer and should be invalidated after DMA transfer.
NOTE: Even if a DMA channel is enabled, it is not operational until the DMA block is enabled using function Cy_DMA_Enable .
NOTE: If the DMA descriptor is configured to generate an interrupt, the interrupt must be enabled using the Cy_DMA_Channel_SetInterruptMask function for each DMA channel. NOTE: When DCache is enabled it is critical to clean the DCache right before calling Cy_DMA_Channel_Enable .Cleaning the cache too early or too late may result in a CY_DMA_INTR_CAUSE_SRC_BUS_ERROR interrupt.
Ensure cache maintenance operations are performed at the correct point in the sequence to avoid data coherency issues.
For example:
#define DATACNT (8UL)
#define CY_DMA_INTR_MASK (0x01UL)
uint32_t src_data[DATACNT];
uint32_t dst_data[DATACNT];
uint8_t currentYIndex;
{
.srcAddress = &src_data,
.dstAddress = &dst_data,
.srcXincrement = 1U,
.dstXincrement = 1U,
.xCount = DATACNT,
.srcYincrement = 0U,
.dstYincrement = 0U,
.yCount = 1UL,
.nextDescriptor = &nextDescriptor,
};
{
}
{
}
{
}
(void) currentYIndex;
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_DMA_Enable(DW_Type *base)
Enables the DMA block.
Definition: cy_dma.h:552
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_DMA_Channel_Enable(DW_Type *base, uint32_t channel)
The function is used to enable a DMA channel.
Definition: cy_dma.h:1545
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_DMA_Channel_SetDescriptor(DW_Type *base, uint32_t channel, cy_stc_dma_descriptor_t const *descriptor)
Sets a descriptor as current for the specified DMA channel.
Definition: cy_dma.h:1520
__STATIC_INLINE bool Cy_DMA_Channel_IsEnabled(DW_Type *base, uint32_t channel)
The function checks whether a channel is in the enabled state.
Definition: cy_dma.h:1593
cy_en_dma_status_t Cy_DMA_Channel_Init(DW_Type *base, uint32_t channel, cy_stc_dma_channel_config_t const *channelConfig)
Initializes the DMA channel with a descriptor and other parameters.
Definition: cy_dma.c:259
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_DMA_Channel_SetInterruptMask(DW_Type *base, uint32_t channel, uint32_t interrupt)
Sets an interrupt mask value for the specified channel.
Definition: cy_dma.h:1859
__STATIC_INLINE uint8_t Cy_DMA_Channel_GetCurrentYIndex(DW_Type const *base, uint32_t channel)
Returns the current Y loop index for the channel.
Definition: cy_dma.h:1701
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_DMA_Channel_SetPriority(DW_Type *base, uint32_t channel, uint32_t priority)
The function is used to set a priority for the DMA channel.
Definition: cy_dma.h:1620
bool enable
This parameter specifies whether the channel is enabled after initializing.
Definition: cy_dma.h:391
bool bufferable
This parameter specifies whether a write transaction can complete.
Definition: cy_dma.h:392
bool preemptable
Specifies whether the channel is preemptable by another higher-priority channel.
Definition: cy_dma.h:389
cy_en_dma_retrigger_t retrigger
Specifies whether the DW controller should wait for the input trigger to be deactivated.
Definition: cy_dma.h:362
This structure holds the initialization values for the DMA channel.
Definition: cy_dma.h:387
This structure is a configuration structure pre-initialized by the user and passed as a parameter to ...
Definition: cy_dma.h:361
DMA descriptor structure type.
Definition: cy_dma.h:343
cy_en_dma_status_t Cy_DMA_Descriptor_Init(cy_stc_dma_descriptor_t *descriptor, cy_stc_dma_descriptor_config_t const *config)
Initializes the descriptor structure in SRAM from a pre-initialized configuration structure.
Definition: cy_dma.c:107
@ CY_DMA_WORD
Full word (four bytes).
Definition: cy_dma.h:223
@ CY_DMA_TRANSFER_SIZE_WORD
A full word (four bytes).
Definition: cy_dma.h:239
@ CY_DMA_DESCR
One descriptor transfer.
Definition: cy_dma.h:214
@ CY_DMA_1D_TRANSFER
1D transfer.
Definition: cy_dma.h:204
@ CY_DMA_CHANNEL_ENABLED
Channel stays enabled.
Definition: cy_dma.h:245
@ CY_DMA_RETRIG_IM
Retrigger immediately.
Definition: cy_dma.h:229
@ CY_DMA_SUCCESS
Success.
Definition: cy_dma.h:252
#define CY_DMA_INTR_MASK
The DMA channel interrupt mask.
Definition: cy_dma.h:158
Data Cache line is 32 bytes. User needs to make sure that the source and destination buffer pointers and the config structure pointers passed to the following functions points to 32 bit aligned data. Cy_DMA_Channel_SetDescriptor, Cy_DMA_Descriptor_SetNextDescriptor, Cy_DMA_Descriptor_SetSrcAddress, Cy_DMA_Descriptor_SetDstAddress. User can use CY_ALIGN(32) macro for 32 bit alignment. User needs to clean the following data elements from the cache and invalidate before accessing them. source and destination buffers and descriptor structure.
int32_t cmpRes;
#if defined (__DCACHE_PRESENT) && (__DCACHE_PRESENT != 0)
SCB_CleanDCache_by_Addr((uint32_t*)src_data, DATACNT);
SCB_CleanDCache_by_Addr((uint32_t*)&dw0_chan0_Descriptor, sizeof(dw0_chan0_Descriptor));
#endif
#if (CY_IP_MXPERI_VERSION == 1U)
#else
#endif
{
}
#if defined (__DCACHE_PRESENT) && (__DCACHE_PRESENT != 0)
SCB_InvalidateDCache_by_Addr ((uint32_t*)dst_data, DATACNT);
#endif
cmpRes = memcmp(src_data, dst_data, DATACNT);
if (cmpRes !=0)
{
}
else
{
}
__STATIC_INLINE uint32_t Cy_DMA_Channel_GetInterruptStatus(DW_Type const *base, uint32_t channel)
Returns the interrupt status of the specified channel.
Definition: cy_dma.h:1727
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_DMA_Descriptor_SetDstAddress(cy_stc_dma_descriptor_t *descriptor, void const *dstAddress)
Sets the destination address for the specified descriptor.
Definition: cy_dma.h:764
__STATIC_INLINE void Cy_DMA_Descriptor_SetSrcAddress(cy_stc_dma_descriptor_t *descriptor, void const *srcAddress)
Sets the source address for the specified descriptor.
Definition: cy_dma.h:719
__STATIC_INLINE cy_en_trigmux_status_t Cy_TrigMux_SwTrigger(uint32_t trigLine, uint32_t cycles)
This function generates a software trigger on an input trigger line.
Definition: cy_trigmux.h:287
#define CY_TRIGGER_TWO_CYCLES
The only valid cycles number value for PERI_ver2.
Definition: cy_trigmux.h:144
More Information.
See: the DMA chapter of the device technical reference manual (TRM); the DMA Component datasheet;
