SSL/TLS functions. More...
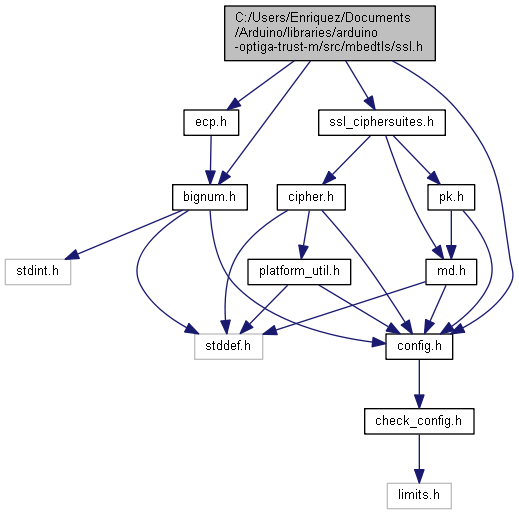
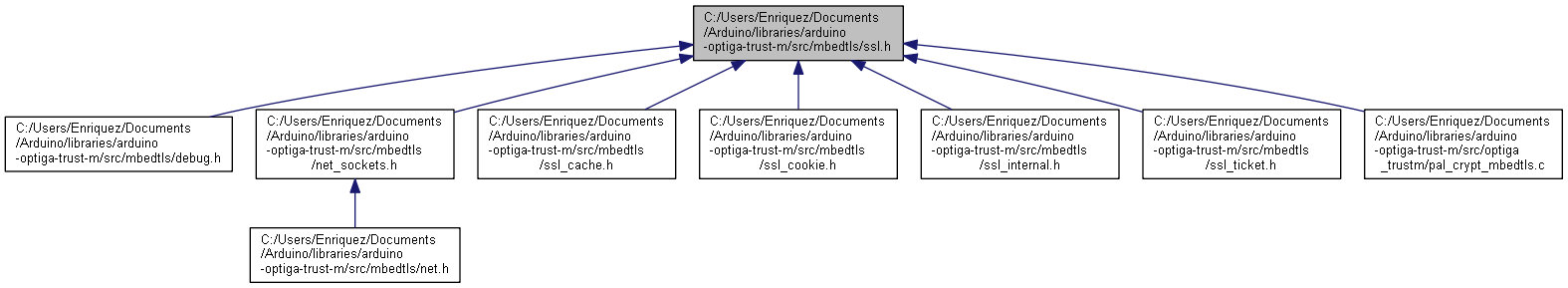
Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| union | mbedtls_ssl_premaster_secret |
| struct | mbedtls_ssl_session |
| struct | mbedtls_ssl_config |
| struct | mbedtls_ssl_context |
Typedefs | |
| typedef int | mbedtls_ssl_send_t(void *ctx, const unsigned char *buf, size_t len) |
| Callback type: send data on the network. More... | |
| typedef int | mbedtls_ssl_recv_t(void *ctx, unsigned char *buf, size_t len) |
| Callback type: receive data from the network. More... | |
| typedef int | mbedtls_ssl_recv_timeout_t(void *ctx, unsigned char *buf, size_t len, uint32_t timeout) |
| Callback type: receive data from the network, with timeout. More... | |
| typedef void | mbedtls_ssl_set_timer_t(void *ctx, uint32_t int_ms, uint32_t fin_ms) |
| Callback type: set a pair of timers/delays to watch. More... | |
| typedef int | mbedtls_ssl_get_timer_t(void *ctx) |
| Callback type: get status of timers/delays. More... | |
| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_session | mbedtls_ssl_session |
| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_context | mbedtls_ssl_context |
| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_config | mbedtls_ssl_config |
| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_transform | mbedtls_ssl_transform |
| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_handshake_params | mbedtls_ssl_handshake_params |
| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_sig_hash_set_t | mbedtls_ssl_sig_hash_set_t |
| typedef int | mbedtls_ssl_ticket_write_t(void *p_ticket, const mbedtls_ssl_session *session, unsigned char *start, const unsigned char *end, size_t *tlen, uint32_t *lifetime) |
| Callback type: generate and write session ticket. More... | |
| typedef int | mbedtls_ssl_ticket_parse_t(void *p_ticket, mbedtls_ssl_session *session, unsigned char *buf, size_t len) |
| Callback type: parse and load session ticket. More... | |
| typedef int | mbedtls_ssl_cookie_write_t(void *ctx, unsigned char **p, unsigned char *end, const unsigned char *info, size_t ilen) |
| Callback type: generate a cookie. More... | |
| typedef int | mbedtls_ssl_cookie_check_t(void *ctx, const unsigned char *cookie, size_t clen, const unsigned char *info, size_t ilen) |
| Callback type: verify a cookie. More... | |
Functions | |
| const char * | mbedtls_ssl_get_ciphersuite_name (const int ciphersuite_id) |
| Return the name of the ciphersuite associated with the given ID. More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_get_ciphersuite_id (const char *ciphersuite_name) |
| Return the ID of the ciphersuite associated with the given name. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_init (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Initialize an SSL context Just makes the context ready for mbedtls_ssl_setup() or mbedtls_ssl_free() More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_setup (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl, const mbedtls_ssl_config *conf) |
| Set up an SSL context for use. More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_session_reset (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Reset an already initialized SSL context for re-use while retaining application-set variables, function pointers and data. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_conf_endpoint (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, int endpoint) |
| Set the current endpoint type. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_conf_transport (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, int transport) |
| Set the transport type (TLS or DTLS). Default: TLS. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_conf_authmode (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, int authmode) |
| Set the certificate verification mode Default: NONE on server, REQUIRED on client. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_conf_rng (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, int(*f_rng)(void *, unsigned char *, size_t), void *p_rng) |
| Set the random number generator callback. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_conf_dbg (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, void(*f_dbg)(void *, int, const char *, int, const char *), void *p_dbg) |
| Set the debug callback. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_set_bio (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl, void *p_bio, mbedtls_ssl_send_t *f_send, mbedtls_ssl_recv_t *f_recv, mbedtls_ssl_recv_timeout_t *f_recv_timeout) |
| Set the underlying BIO callbacks for write, read and read-with-timeout. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_conf_read_timeout (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, uint32_t timeout) |
| Set the timeout period for mbedtls_ssl_read() (Default: no timeout.) More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_set_timer_cb (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl, void *p_timer, mbedtls_ssl_set_timer_t *f_set_timer, mbedtls_ssl_get_timer_t *f_get_timer) |
| Set the timer callbacks (Mandatory for DTLS.) More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_conf_ciphersuites (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, const int *ciphersuites) |
| Set the list of allowed ciphersuites and the preference order. First in the list has the highest preference. (Overrides all version-specific lists) More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_conf_ciphersuites_for_version (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, const int *ciphersuites, int major, int minor) |
| Set the list of allowed ciphersuites and the preference order for a specific version of the protocol. (Only useful on the server side) More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_conf_max_version (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, int major, int minor) |
| Set the maximum supported version sent from the client side and/or accepted at the server side (Default: MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_MAJOR_VERSION, MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_MINOR_VERSION) More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_conf_min_version (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, int major, int minor) |
| Set the minimum accepted SSL/TLS protocol version (Default: TLS 1.0) More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_conf_legacy_renegotiation (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, int allow_legacy) |
| Prevent or allow legacy renegotiation. (Default: MBEDTLS_SSL_LEGACY_NO_RENEGOTIATION) More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_check_pending (const mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Check if there is data already read from the underlying transport but not yet processed. More... | |
| size_t | mbedtls_ssl_get_bytes_avail (const mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Return the number of application data bytes remaining to be read from the current record. More... | |
| uint32_t | mbedtls_ssl_get_verify_result (const mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Return the result of the certificate verification. More... | |
| const char * | mbedtls_ssl_get_ciphersuite (const mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Return the name of the current ciphersuite. More... | |
| const char * | mbedtls_ssl_get_version (const mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Return the current SSL version (SSLv3/TLSv1/etc) More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_get_record_expansion (const mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Return the (maximum) number of bytes added by the record layer: header + encryption/MAC overhead (inc. padding) More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_get_max_out_record_payload (const mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
Return the current maximum outgoing record payload in bytes. This takes into account the config.h setting MBEDTLS_SSL_OUT_CONTENT_LEN, the configured and negotiated max fragment length extension if used, and for DTLS the path MTU as configured and current record expansion. More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_handshake (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Perform the SSL handshake. More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_handshake_step (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Perform a single step of the SSL handshake. More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_read (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl, unsigned char *buf, size_t len) |
| Read at most 'len' application data bytes. More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_write (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl, const unsigned char *buf, size_t len) |
| Try to write exactly 'len' application data bytes. More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_send_alert_message (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl, unsigned char level, unsigned char message) |
| Send an alert message. More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_close_notify (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Notify the peer that the connection is being closed. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_free (mbedtls_ssl_context *ssl) |
| Free referenced items in an SSL context and clear memory. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_config_init (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf) |
| Initialize an SSL configuration context Just makes the context ready for mbedtls_ssl_config_defaults() or mbedtls_ssl_config_free(). More... | |
| int | mbedtls_ssl_config_defaults (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf, int endpoint, int transport, int preset) |
| Load reasonnable default SSL configuration values. (You need to call mbedtls_ssl_config_init() first.) More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_config_free (mbedtls_ssl_config *conf) |
| Free an SSL configuration context. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_session_init (mbedtls_ssl_session *session) |
| Initialize SSL session structure. More... | |
| void | mbedtls_ssl_session_free (mbedtls_ssl_session *session) |
| Free referenced items in an SSL session including the peer certificate and clear memory. More... | |
SSL/TLS functions.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_ALLOC_FAILED -0x7F00 |
Memory allocation failed
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_ASYNC_IN_PROGRESS -0x6500 |
The asynchronous operation is not completed yet.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_CERTIFICATE -0x7A00 |
Processing of the Certificate handshake message failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_CERTIFICATE_REQUEST -0x7A80 |
Processing of the CertificateRequest handshake message failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_CERTIFICATE_VERIFY -0x7D80 |
Processing of the CertificateVerify handshake message failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_CHANGE_CIPHER_SPEC -0x7E00 |
Processing of the ChangeCipherSpec handshake message failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_CLIENT_HELLO -0x7900 |
Processing of the ClientHello handshake message failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_CLIENT_KEY_EXCHANGE -0x7C00 |
Processing of the ClientKeyExchange handshake message failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_CLIENT_KEY_EXCHANGE_CS -0x7D00 |
Processing of the ClientKeyExchange handshake message failed in DHM / ECDH Calculate Secret.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_CLIENT_KEY_EXCHANGE_RP -0x7C80 |
Processing of the ClientKeyExchange handshake message failed in DHM / ECDH Read Public.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_FINISHED -0x7E80 |
Processing of the Finished handshake message failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_NEW_SESSION_TICKET -0x6E00 |
Processing of the NewSessionTicket handshake message failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_PROTOCOL_VERSION -0x6E80 |
Handshake protocol not within min/max boundaries
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_SERVER_HELLO -0x7980 |
Processing of the ServerHello handshake message failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_SERVER_HELLO_DONE -0x7B80 |
Processing of the ServerHelloDone handshake message failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_HS_SERVER_KEY_EXCHANGE -0x7B00 |
Processing of the ServerKeyExchange handshake message failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BAD_INPUT_DATA -0x7100 |
Bad input parameters to function.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL -0x6A00 |
A buffer is too small to receive or write a message
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_CA_CHAIN_REQUIRED -0x7680 |
No CA Chain is set, but required to operate.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_CERTIFICATE_REQUIRED -0x7580 |
The own certificate is not set, but needed by the server.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_CERTIFICATE_TOO_LARGE -0x7500 |
Our own certificate(s) is/are too large to send in an SSL message.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_CLIENT_RECONNECT -0x6780 |
The client initiated a reconnect from the same port.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_COMPRESSION_FAILED -0x6F00 |
Processing of the compression / decompression failed
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_CONN_EOF -0x7280 |
The connection indicated an EOF.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_CONTINUE_PROCESSING -0x6580 |
Internal-only message signaling that further message-processing should be done
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_COUNTER_WRAPPING -0x6B80 |
A counter would wrap (eg, too many messages exchanged).
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_CRYPTO_IN_PROGRESS -0x7000 |
A cryptographic operation is in progress. Try again later.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_EARLY_MESSAGE -0x6480 |
Internal-only message signaling that a message arrived early.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_FATAL_ALERT_MESSAGE -0x7780 |
A fatal alert message was received from our peer.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_FEATURE_UNAVAILABLE -0x7080 |
The requested feature is not available.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_HELLO_VERIFY_REQUIRED -0x6A80 |
DTLS client must retry for hello verification
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_HW_ACCEL_FAILED -0x7F80 |
Hardware acceleration function returned with error
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_HW_ACCEL_FALLTHROUGH -0x6F80 |
Hardware acceleration function skipped / left alone data
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_INTERNAL_ERROR -0x6C00 |
Internal error (eg, unexpected failure in lower-level module)
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_INVALID_MAC -0x7180 |
Verification of the message MAC failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_INVALID_RECORD -0x7200 |
An invalid SSL record was received.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_INVALID_VERIFY_HASH -0x6600 |
Couldn't set the hash for verifying CertificateVerify
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_NO_CIPHER_CHOSEN -0x7380 |
The server has no ciphersuites in common with the client.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_NO_CLIENT_CERTIFICATE -0x7480 |
No client certification received from the client, but required by the authentication mode.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_NO_RNG -0x7400 |
No RNG was provided to the SSL module.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_NO_USABLE_CIPHERSUITE -0x6980 |
None of the common ciphersuites is usable (eg, no suitable certificate, see debug messages).
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_NON_FATAL -0x6680 |
The alert message received indicates a non-fatal error.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_PEER_CLOSE_NOTIFY -0x7880 |
The peer notified us that the connection is going to be closed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_PEER_VERIFY_FAILED -0x7800 |
Verification of our peer failed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_PK_TYPE_MISMATCH -0x6D00 |
Public key type mismatch (eg, asked for RSA key exchange and presented EC key)
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_PRIVATE_KEY_REQUIRED -0x7600 |
The own private key or pre-shared key is not set, but needed.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_SESSION_TICKET_EXPIRED -0x6D80 |
Session ticket has expired.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_TIMEOUT -0x6800 |
The operation timed out.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_UNEXPECTED_MESSAGE -0x7700 |
An unexpected message was received from our peer.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_UNEXPECTED_RECORD -0x6700 |
Record header looks valid but is not expected.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_UNKNOWN_CIPHER -0x7300 |
An unknown cipher was received.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_UNKNOWN_IDENTITY -0x6C80 |
Unknown identity received (eg, PSK identity)
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_WAITING_SERVER_HELLO_RENEGO -0x6B00 |
Unexpected message at ServerHello in renegotiation.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_WANT_READ -0x6900 |
No data of requested type currently available on underlying transport.
| #define MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_WANT_WRITE -0x6880 |
Connection requires a write call.
| #define MBEDTLS_PREMASTER_SIZE sizeof( union mbedtls_ssl_premaster_secret ) |
| #define MBEDTLS_PSK_MAX_LEN 32 /* 256 bits */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_LEVEL_FATAL 2 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_LEVEL_WARNING 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_ACCESS_DENIED 49 /* 0x31 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_BAD_CERT 42 /* 0x2A */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_BAD_RECORD_MAC 20 /* 0x14 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_CERT_EXPIRED 45 /* 0x2D */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_CERT_REVOKED 44 /* 0x2C */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_CERT_UNKNOWN 46 /* 0x2E */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_CLOSE_NOTIFY 0 /* 0x00 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_DECODE_ERROR 50 /* 0x32 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_DECOMPRESSION_FAILURE 30 /* 0x1E */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_DECRYPT_ERROR 51 /* 0x33 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_DECRYPTION_FAILED 21 /* 0x15 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_EXPORT_RESTRICTION 60 /* 0x3C */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_HANDSHAKE_FAILURE 40 /* 0x28 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_ILLEGAL_PARAMETER 47 /* 0x2F */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_INAPROPRIATE_FALLBACK 86 /* 0x56 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_INSUFFICIENT_SECURITY 71 /* 0x47 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_INTERNAL_ERROR 80 /* 0x50 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_NO_APPLICATION_PROTOCOL 120 /* 0x78 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_NO_CERT 41 /* 0x29 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_NO_RENEGOTIATION 100 /* 0x64 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_PROTOCOL_VERSION 70 /* 0x46 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_RECORD_OVERFLOW 22 /* 0x16 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_UNEXPECTED_MESSAGE 10 /* 0x0A */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_UNKNOWN_CA 48 /* 0x30 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_UNKNOWN_PSK_IDENTITY 115 /* 0x73 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_UNRECOGNIZED_NAME 112 /* 0x70 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_UNSUPPORTED_CERT 43 /* 0x2B */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_UNSUPPORTED_EXT 110 /* 0x6E */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_MSG_USER_CANCELED 90 /* 0x5A */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ANTI_REPLAY_DISABLED 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ANTI_REPLAY_ENABLED 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ARC4_DISABLED 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ARC4_ENABLED 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_CBC_RECORD_SPLITTING_DISABLED 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_CBC_RECORD_SPLITTING_ENABLED 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_CERT_REQ_CA_LIST_DISABLED 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_CERT_REQ_CA_LIST_ENABLED 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_CERT_TYPE_ECDSA_SIGN 64 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_CERT_TYPE_RSA_SIGN 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_COMPRESS_DEFLATE 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_COMPRESS_NULL 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_DEFAULT_TICKET_LIFETIME 86400 |
Lifetime of session tickets (if enabled)
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_DTLS_MAX_BUFFERING 32768 |
Maximum number of heap-allocated bytes for the purpose of DTLS handshake message reassembly and future message buffering.
This should be at least 9/8 * MBEDTLSSL_IN_CONTENT_LEN to account for a reassembled handshake message of maximum size, together with its reassembly bitmap.
A value of 2 * MBEDTLS_SSL_IN_CONTENT_LEN (32768 by default) should be sufficient for all practical situations as it allows to reassembly a large handshake message (such as a certificate) while buffering multiple smaller handshake messages.
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_DTLS_TIMEOUT_DFL_MAX 60000 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_DTLS_TIMEOUT_DFL_MIN 1000 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_EMPTY_RENEGOTIATION_INFO 0xFF |
renegotiation info ext
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ETM_DISABLED 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_ETM_ENABLED 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_EXTENDED_MS_DISABLED 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_EXTENDED_MS_ENABLED 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_FALLBACK_SCSV_VALUE 0x5600 |
RFC 7507 section 2
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HASH_MD5 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HASH_NONE 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HASH_SHA1 2 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HASH_SHA224 3 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HASH_SHA256 4 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HASH_SHA384 5 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HASH_SHA512 6 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_CERTIFICATE 11 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_CERTIFICATE_REQUEST 13 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_CERTIFICATE_VERIFY 15 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_CLIENT_HELLO 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_CLIENT_KEY_EXCHANGE 16 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_FINISHED 20 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_HELLO_REQUEST 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_HELLO_VERIFY_REQUEST 3 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_NEW_SESSION_TICKET 4 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_SERVER_HELLO 2 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_SERVER_HELLO_DONE 14 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_HS_SERVER_KEY_EXCHANGE 12 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_IN_CONTENT_LEN MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_CONTENT_LEN |
Maximum length (in bytes) of incoming plaintext fragments.
This determines the size of the incoming TLS I/O buffer in such a way that it is capable of holding the specified amount of plaintext data, regardless of the protection mechanism used.
If this option is undefined, it inherits its value from MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_CONTENT_LEN.
Uncomment to set the maximum plaintext size of the incoming I/O buffer independently of the outgoing I/O buffer.
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_CLIENT 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_FALLBACK 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_NOT_FALLBACK 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_SERVER 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_LEGACY_ALLOW_RENEGOTIATION 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_LEGACY_BREAK_HANDSHAKE 2 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_LEGACY_NO_RENEGOTIATION 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_LEGACY_RENEGOTIATION 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MAJOR_VERSION_3 3 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_CONTENT_LEN 16384 |
This macro is invoked by the library when an invalid parameter is detected that is only checked with MBEDTLS_CHECK_PARAMS (see the documentation of that option for context).
When you leave this undefined here, a default definition is provided that invokes the function mbedtls_param_failed(), which is declared in platform_util.h for the benefit of the library, but that you need to define in your application.
When you define this here, this replaces the default definition in platform_util.h (which no longer declares the function mbedtls_param_failed()) and it is your responsibility to make sure this macro expands to something suitable (in particular, that all the necessary declarations are visible from within the library - you can ensure that by providing them in this file next to the macro definition).
Note that you may define this macro to expand to nothing, in which case you don't have to worry about declarations or definitions. However, you will then be notified about invalid parameters only in non-void functions, and void function will just silently return early on invalid parameters, which partially negates the benefits of enabling #MBEDTLS_CHECK_PARAMS in the first place, so is discouraged.
| cond | The expression that should evaluate to true, but doesn't. |
Maximum length (in bytes) of incoming and outgoing plaintext fragments.
This determines the size of both the incoming and outgoing TLS I/O buffers in such a way that both are capable of holding the specified amount of plaintext data, regardless of the protection mechanism used.
To configure incoming and outgoing I/O buffers separately, use MBEDTLS_SSL_IN_CONTENT_LEN and MBEDTLS_SSL_OUT_CONTENT_LEN, which overwrite the value set by this option.
Uncomment to set the maximum plaintext size of both incoming and outgoing I/O buffers.
Size of the input / output buffer
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_FRAG_LEN_1024 2 |
MaxFragmentLength 2^10
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_FRAG_LEN_2048 3 |
MaxFragmentLength 2^11
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_FRAG_LEN_4096 4 |
MaxFragmentLength 2^12
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_FRAG_LEN_512 1 |
MaxFragmentLength 2^9
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_FRAG_LEN_INVALID 5 |
first invalid value
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_FRAG_LEN_NONE 0 |
don't use this extension
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_HOST_NAME_LEN 255 |
Maximum host name defined in RFC 1035
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_0 0 |
SSL v3.0
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_1 1 |
TLS v1.0
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_2 2 |
TLS v1.1
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_3 3 |
TLS v1.2
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MSG_ALERT 21 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MSG_APPLICATION_DATA 23 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MSG_CHANGE_CIPHER_SPEC 20 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_MSG_HANDSHAKE 22 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_OUT_CONTENT_LEN MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_CONTENT_LEN |
Maximum length (in bytes) of outgoing plaintext fragments.
This determines the size of the outgoing TLS I/O buffer in such a way that it is capable of holding the specified amount of plaintext data, regardless of the protection mechanism used.
If this option undefined, it inherits its value from MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_CONTENT_LEN.
It is possible to save RAM by setting a smaller outward buffer, while keeping the default inward 16384 byte buffer to conform to the TLS specification.
The minimum required outward buffer size is determined by the handshake protocol's usage. Handshaking will fail if the outward buffer is too small. The specific size requirement depends on the configured ciphers and any certificate data which is sent during the handshake.
Uncomment to set the maximum plaintext size of the outgoing I/O buffer independently of the incoming I/O buffer.
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_PRESET_DEFAULT 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_PRESET_SUITEB 2 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_RENEGO_MAX_RECORDS_DEFAULT 16 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_RENEGOTIATION_DISABLED 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_RENEGOTIATION_ENABLED 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_RENEGOTIATION_NOT_ENFORCED -1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_SECURE_RENEGOTIATION 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_SESSION_TICKETS_DISABLED 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_SESSION_TICKETS_ENABLED 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_SIG_ANON 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_SIG_ECDSA 3 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_SIG_RSA 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_TRANSPORT_DATAGRAM 1 |
DTLS
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_TRANSPORT_STREAM 0 |
TLS
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_TRUNC_HMAC_DISABLED 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_TRUNC_HMAC_ENABLED 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_TRUNCATED_HMAC_LEN 10 /* 80 bits, rfc 6066 section 7 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_VERIFY_DATA_MAX_LEN 12 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_VERIFY_NONE 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_VERIFY_OPTIONAL 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_VERIFY_REQUIRED 2 |
| #define MBEDTLS_SSL_VERIFY_UNSET 3 /* Used only for sni_authmode */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_ALPN 16 |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_ECJPAKE_KKPP 256 /* experimental */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_ENCRYPT_THEN_MAC 22 /* 0x16 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_EXTENDED_MASTER_SECRET 0x0017 /* 23 */ |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_MAX_FRAGMENT_LENGTH 1 |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_RENEGOTIATION_INFO 0xFF01 |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_SERVERNAME 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_SERVERNAME_HOSTNAME 0 |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_SESSION_TICKET 35 |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_SIG_ALG 13 |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_SUPPORTED_ELLIPTIC_CURVES 10 |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_SUPPORTED_POINT_FORMATS 11 |
| #define MBEDTLS_TLS_EXT_TRUNCATED_HMAC 4 |
| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_config mbedtls_ssl_config |
| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_context mbedtls_ssl_context |
| typedef int mbedtls_ssl_cookie_check_t(void *ctx, const unsigned char *cookie, size_t clen, const unsigned char *info, size_t ilen) |
Callback type: verify a cookie.
| ctx | Context for the callback |
| cookie | Cookie to verify |
| clen | Length of cookie |
| info | Client ID info that was passed to mbedtls_ssl_set_client_transport_id() |
| ilen | Length of info in bytes |
| typedef int mbedtls_ssl_cookie_write_t(void *ctx, unsigned char **p, unsigned char *end, const unsigned char *info, size_t ilen) |
Callback type: generate a cookie.
| ctx | Context for the callback |
| p | Buffer to write to, must be updated to point right after the cookie |
| end | Pointer to one past the end of the output buffer |
| info | Client ID info that was passed to mbedtls_ssl_set_client_transport_id() |
| ilen | Length of info in bytes |
| typedef int mbedtls_ssl_get_timer_t(void *ctx) |
Callback type: get status of timers/delays.
| ctx | Context pointer |
| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_handshake_params mbedtls_ssl_handshake_params |
| typedef int mbedtls_ssl_recv_t(void *ctx, unsigned char *buf, size_t len) |
Callback type: receive data from the network.
| ctx | Context for the receive callback (typically a file descriptor) |
| buf | Buffer to write the received data to |
| len | Length of the receive buffer |
MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_WANT_READ must be returned when the operation would block.| typedef int mbedtls_ssl_recv_timeout_t(void *ctx, unsigned char *buf, size_t len, uint32_t timeout) |
Callback type: receive data from the network, with timeout.
| ctx | Context for the receive callback (typically a file descriptor) |
| buf | Buffer to write the received data to |
| len | Length of the receive buffer |
| timeout | Maximum nomber of millisecondes to wait for data 0 means no timeout (potentially waiting forever) |
MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_TIMEOUT if the operation timed out, MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_WANT_READ if interrupted by a signal.| typedef int mbedtls_ssl_send_t(void *ctx, const unsigned char *buf, size_t len) |
Callback type: send data on the network.
| ctx | Context for the send callback (typically a file descriptor) |
| buf | Buffer holding the data to send |
| len | Length of the data to send |
MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_WANT_WRITE must be returned when the operation would block.| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_session mbedtls_ssl_session |
| typedef void mbedtls_ssl_set_timer_t(void *ctx, uint32_t int_ms, uint32_t fin_ms) |
Callback type: set a pair of timers/delays to watch.
| ctx | Context pointer |
| int_ms | Intermediate delay in milliseconds |
| fin_ms | Final delay in milliseconds 0 cancels the current timer. |
mbedtls_ssl_get_timer_t callback to return correct information.mbedtls_ssl_handshake() with the proper SSL context to be scheduled. Care must be taken to ensure that at most one such call happens at a time.| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_sig_hash_set_t mbedtls_ssl_sig_hash_set_t |
| typedef int mbedtls_ssl_ticket_parse_t(void *p_ticket, mbedtls_ssl_session *session, unsigned char *buf, size_t len) |
Callback type: parse and load session ticket.
| p_ticket | Context for the callback |
| session | SSL session to be loaded |
| buf | Start of the buffer containing the ticket |
| len | Length of the ticket. |
| typedef int mbedtls_ssl_ticket_write_t(void *p_ticket, const mbedtls_ssl_session *session, unsigned char *start, const unsigned char *end, size_t *tlen, uint32_t *lifetime) |
Callback type: generate and write session ticket.
| p_ticket | Context for the callback |
| session | SSL session to be written in the ticket |
| start | Start of the output buffer |
| end | End of the output buffer |
| tlen | On exit, holds the length written |
| lifetime | On exit, holds the lifetime of the ticket in seconds |
| typedef struct mbedtls_ssl_transform mbedtls_ssl_transform |
| enum mbedtls_ssl_states |
| int mbedtls_ssl_check_pending | ( | const mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Check if there is data already read from the underlying transport but not yet processed.
| ssl | SSL context |
mbedtls_ssl_get_bytes_avail in that it considers any kind of unprocessed data, not only unread application data. If mbedtls_ssl_get_bytes returns a non-zero value, this function will also signal pending data, but the converse does not hold. For example, in DTLS there might be further records waiting to be processed from the current underlying transport's datagram.mbedtls_ssl_read will provide any data; e.g., the unprocessed data might turn out to be an alert or a handshake message.| int mbedtls_ssl_close_notify | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Notify the peer that the connection is being closed.
| ssl | SSL context |
mbedtls_ssl_session_reset() on it before re-using it for a new connection; the current connection must be closed. | void mbedtls_ssl_conf_authmode | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| int | authmode | ||
| ) |
Set the certificate verification mode Default: NONE on server, REQUIRED on client.
| conf | SSL configuration |
| authmode | can be: |
MBEDTLS_SSL_VERIFY_NONE: peer certificate is not checked (default on server) (insecure on client)
MBEDTLS_SSL_VERIFY_OPTIONAL: peer certificate is checked, however the handshake continues even if verification failed; mbedtls_ssl_get_verify_result() can be called after the handshake is complete.
MBEDTLS_SSL_VERIFY_REQUIRED: peer must present a valid certificate, handshake is aborted if verification failed. (default on client)
| void mbedtls_ssl_conf_ciphersuites | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| const int * | ciphersuites | ||
| ) |
Set the list of allowed ciphersuites and the preference order. First in the list has the highest preference. (Overrides all version-specific lists)
The ciphersuites array is not copied, and must remain valid for the lifetime of the ssl_config.
Note: The server uses its own preferences over the preference of the client unless MBEDTLS_SSL_SRV_RESPECT_CLIENT_PREFERENCE is defined!
| conf | SSL configuration |
| ciphersuites | 0-terminated list of allowed ciphersuites |
| void mbedtls_ssl_conf_ciphersuites_for_version | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| const int * | ciphersuites, | ||
| int | major, | ||
| int | minor | ||
| ) |
Set the list of allowed ciphersuites and the preference order for a specific version of the protocol. (Only useful on the server side)
The ciphersuites array is not copied, and must remain valid for the lifetime of the ssl_config.
| conf | SSL configuration |
| ciphersuites | 0-terminated list of allowed ciphersuites |
| major | Major version number (only MBEDTLS_SSL_MAJOR_VERSION_3 supported) |
| minor | Minor version number (MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_0, MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_1 and MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_2, MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_3 supported) |
| void mbedtls_ssl_conf_dbg | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| void(*)(void *, int, const char *, int, const char *) | f_dbg, | ||
| void * | p_dbg | ||
| ) |
Set the debug callback.
The callback has the following argument:
void * opaque context for the callback
int debug level
const char * file name
int line number
const char * message
| conf | SSL configuration |
| f_dbg | debug function |
| p_dbg | debug parameter |
| void mbedtls_ssl_conf_endpoint | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| int | endpoint | ||
| ) |
Set the current endpoint type.
| conf | SSL configuration |
| endpoint | must be MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_CLIENT or MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_SERVER |
| void mbedtls_ssl_conf_legacy_renegotiation | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| int | allow_legacy | ||
| ) |
Prevent or allow legacy renegotiation. (Default: MBEDTLS_SSL_LEGACY_NO_RENEGOTIATION)
MBEDTLS_SSL_LEGACY_NO_RENEGOTIATION allows connections to be established even if the peer does not support secure renegotiation, but does not allow renegotiation to take place if not secure. (Interoperable and secure option)
MBEDTLS_SSL_LEGACY_ALLOW_RENEGOTIATION allows renegotiations with non-upgraded peers. Allowing legacy renegotiation makes the connection vulnerable to specific man in the middle attacks. (See RFC 5746) (Most interoperable and least secure option)
MBEDTLS_SSL_LEGACY_BREAK_HANDSHAKE breaks off connections if peer does not support secure renegotiation. Results in interoperability issues with non-upgraded peers that do not support renegotiation altogether. (Most secure option, interoperability issues)
| conf | SSL configuration |
| allow_legacy | Prevent or allow (SSL_NO_LEGACY_RENEGOTIATION, SSL_ALLOW_LEGACY_RENEGOTIATION or MBEDTLS_SSL_LEGACY_BREAK_HANDSHAKE) |
| void mbedtls_ssl_conf_max_version | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| int | major, | ||
| int | minor | ||
| ) |
Set the maximum supported version sent from the client side and/or accepted at the server side (Default: MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_MAJOR_VERSION, MBEDTLS_SSL_MAX_MINOR_VERSION)
| conf | SSL configuration |
| major | Major version number (only MBEDTLS_SSL_MAJOR_VERSION_3 supported) |
| minor | Minor version number (MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_0, MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_1 and MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_2, MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_3 supported) |
| void mbedtls_ssl_conf_min_version | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| int | major, | ||
| int | minor | ||
| ) |
Set the minimum accepted SSL/TLS protocol version (Default: TLS 1.0)
| conf | SSL configuration |
| major | Major version number (only MBEDTLS_SSL_MAJOR_VERSION_3 supported) |
| minor | Minor version number (MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_0, MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_1 and MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_2, MBEDTLS_SSL_MINOR_VERSION_3 supported) |
| void mbedtls_ssl_conf_read_timeout | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| uint32_t | timeout | ||
| ) |
Set the timeout period for mbedtls_ssl_read() (Default: no timeout.)
| conf | SSL configuration context |
| timeout | Timeout value in milliseconds. Use 0 for no timeout (default). |
f_recv_timeout was set with mbedtls_ssl_set_bio(). With non-blocking I/O, this will only work if timer callbacks were set with mbedtls_ssl_set_timer_cb().| void mbedtls_ssl_conf_rng | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| int(*)(void *, unsigned char *, size_t) | f_rng, | ||
| void * | p_rng | ||
| ) |
Set the random number generator callback.
| conf | SSL configuration |
| f_rng | RNG function |
| p_rng | RNG parameter |
| void mbedtls_ssl_conf_transport | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| int | transport | ||
| ) |
Set the transport type (TLS or DTLS). Default: TLS.
mbedtls_ssl_set_bio(). You also need to provide timer callbacks with mbedtls_ssl_set_timer_cb().| conf | SSL configuration |
| transport | transport type: MBEDTLS_SSL_TRANSPORT_STREAM for TLS, MBEDTLS_SSL_TRANSPORT_DATAGRAM for DTLS. |
| int mbedtls_ssl_config_defaults | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf, |
| int | endpoint, | ||
| int | transport, | ||
| int | preset | ||
| ) |
Load reasonnable default SSL configuration values. (You need to call mbedtls_ssl_config_init() first.)
| conf | SSL configuration context |
| endpoint | MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_CLIENT or MBEDTLS_SSL_IS_SERVER |
| transport | MBEDTLS_SSL_TRANSPORT_STREAM for TLS, or MBEDTLS_SSL_TRANSPORT_DATAGRAM for DTLS |
| preset | a MBEDTLS_SSL_PRESET_XXX value |
mbedtls_ssl_conf_transport() for notes on DTLS.| void mbedtls_ssl_config_free | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf | ) |
Free an SSL configuration context.
| conf | SSL configuration context |
| void mbedtls_ssl_config_init | ( | mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf | ) |
Initialize an SSL configuration context Just makes the context ready for mbedtls_ssl_config_defaults() or mbedtls_ssl_config_free().
| conf | SSL configuration context |
| void mbedtls_ssl_free | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Free referenced items in an SSL context and clear memory.
| ssl | SSL context |
| size_t mbedtls_ssl_get_bytes_avail | ( | const mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Return the number of application data bytes remaining to be read from the current record.
| ssl | SSL context |
mbedtls_ssl_read has written the maximal amount of data fitting into the input buffer. | const char* mbedtls_ssl_get_ciphersuite | ( | const mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Return the name of the current ciphersuite.
| ssl | SSL context |
| int mbedtls_ssl_get_ciphersuite_id | ( | const char * | ciphersuite_name | ) |
Return the ID of the ciphersuite associated with the given name.
| ciphersuite_name | SSL ciphersuite name |
| const char* mbedtls_ssl_get_ciphersuite_name | ( | const int | ciphersuite_id | ) |
Return the name of the ciphersuite associated with the given ID.
| ciphersuite_id | SSL ciphersuite ID |
| int mbedtls_ssl_get_max_out_record_payload | ( | const mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Return the current maximum outgoing record payload in bytes. This takes into account the config.h setting MBEDTLS_SSL_OUT_CONTENT_LEN, the configured and negotiated max fragment length extension if used, and for DTLS the path MTU as configured and current record expansion.
mbedtls_ssl_write() will return an error if called with a larger length value. With TLS, mbedtls_ssl_write() will fragment the input if necessary and return the number of bytes written; it is up to the caller to call mbedtls_ssl_write() again in order to send the remaining bytes if any.| ssl | SSL context |
| int mbedtls_ssl_get_record_expansion | ( | const mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Return the (maximum) number of bytes added by the record layer: header + encryption/MAC overhead (inc. padding)
| ssl | SSL context |
| uint32_t mbedtls_ssl_get_verify_result | ( | const mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Return the result of the certificate verification.
| ssl | The SSL context to use. |
0 if the certificate verification was successful. -1u if the result is not available. This may happen e.g. if the handshake aborts early, or a verification callback returned a fatal error. MBEDTLS_X509_BADCERT_XXX and MBEDTLS_X509_BADCRL_XXX failure flags; see x509.h. | const char* mbedtls_ssl_get_version | ( | const mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Return the current SSL version (SSLv3/TLSv1/etc)
| ssl | SSL context |
| int mbedtls_ssl_handshake | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Perform the SSL handshake.
| ssl | SSL context |
0 if successful. 0, MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_WANT_READ, MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_WANT_WRITE, MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_ASYNC_IN_PROGRESS or MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_CRYPTO_IN_PROGRESS, you must stop using the SSL context for reading or writing, and either free it or call mbedtls_ssl_session_reset() on it before re-using it for a new connection; the current connection must be closed.| int mbedtls_ssl_handshake_step | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Perform a single step of the SSL handshake.
0. Do not call this function if state is MBEDTLS_SSL_HANDSHAKE_OVER.| ssl | SSL context |
0, MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_WANT_READ, MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_WANT_WRITE, MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_ASYNC_IN_PROGRESS or MBEDTLS_ERR_SSL_CRYPTO_IN_PROGRESS, you must stop using the SSL context for reading or writing, and either free it or call mbedtls_ssl_session_reset() on it before re-using it for a new connection; the current connection must be closed. | void mbedtls_ssl_init | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Initialize an SSL context Just makes the context ready for mbedtls_ssl_setup() or mbedtls_ssl_free()
| ssl | SSL context |
| int mbedtls_ssl_read | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl, |
| unsigned char * | buf, | ||
| size_t | len | ||
| ) |
Read at most 'len' application data bytes.
| ssl | SSL context |
| buf | buffer that will hold the data |
| len | maximum number of bytes to read |
0 if the read end of the underlying transport was closedmbedtls_ssl_session_reset() on it before re-using it for a new connection; the current connection must be closed.mbedtls_ssl_handshake() with the same context (as it has been reset internally). Either way, you must make sure this is seen by the application as a new connection: application state, if any, should be reset, and most importantly the identity of the client must be checked again. WARNING: not validating the identity of the client again, or not transmitting the new identity to the application layer, would allow authentication bypass!mbedtls_ssl_check_pending to check for remaining records. | int mbedtls_ssl_send_alert_message | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl, |
| unsigned char | level, | ||
| unsigned char | message | ||
| ) |
Send an alert message.
| ssl | SSL context |
| level | The alert level of the message (MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_LEVEL_WARNING or MBEDTLS_SSL_ALERT_LEVEL_FATAL) |
| message | The alert message (SSL_ALERT_MSG_*) |
mbedtls_ssl_session_reset() on it before re-using it for a new connection; the current connection must be closed. | void mbedtls_ssl_session_free | ( | mbedtls_ssl_session * | session | ) |
Free referenced items in an SSL session including the peer certificate and clear memory.
| session | SSL session |
| void mbedtls_ssl_session_init | ( | mbedtls_ssl_session * | session | ) |
Initialize SSL session structure.
| session | SSL session |
| int mbedtls_ssl_session_reset | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl | ) |
Reset an already initialized SSL context for re-use while retaining application-set variables, function pointers and data.
| ssl | SSL context |
| void mbedtls_ssl_set_bio | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl, |
| void * | p_bio, | ||
| mbedtls_ssl_send_t * | f_send, | ||
| mbedtls_ssl_recv_t * | f_recv, | ||
| mbedtls_ssl_recv_timeout_t * | f_recv_timeout | ||
| ) |
Set the underlying BIO callbacks for write, read and read-with-timeout.
| ssl | SSL context |
| p_bio | parameter (context) shared by BIO callbacks |
| f_send | write callback |
| f_recv | read callback |
| f_recv_timeout | blocking read callback with timeout. |
mbedtls_ssl_sent_t, mbedtls_ssl_recv_t and mbedtls_ssl_recv_timeout_t for the conventions those callbacks must follow.mbedtls_net_send(), mbedtls_net_recv() and mbedtls_net_recv_timeout() that are suitable to be used here. | void mbedtls_ssl_set_timer_cb | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl, |
| void * | p_timer, | ||
| mbedtls_ssl_set_timer_t * | f_set_timer, | ||
| mbedtls_ssl_get_timer_t * | f_get_timer | ||
| ) |
Set the timer callbacks (Mandatory for DTLS.)
| ssl | SSL context |
| p_timer | parameter (context) shared by timer callbacks |
| f_set_timer | set timer callback |
| f_get_timer | get timer callback. Must return: |
mbedtls_ssl_set_timer_t and mbedtls_ssl_get_timer_t for the conventions this pair of callbacks must follow.mbedtls_timing_set_delay() and mbedtls_timing_get_delay() that are suitable for using here, except if using an event-driven style.| int mbedtls_ssl_setup | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl, |
| const mbedtls_ssl_config * | conf | ||
| ) |
Set up an SSL context for use.
| ssl | SSL context |
| conf | SSL configuration to use |
| int mbedtls_ssl_write | ( | mbedtls_ssl_context * | ssl, |
| const unsigned char * | buf, | ||
| size_t | len | ||
| ) |
Try to write exactly 'len' application data bytes.
| ssl | SSL context |
| buf | buffer holding the data |
| len | how many bytes must be written |
len). mbedtls_ssl_session_reset() on it before re-using it for a new connection; the current connection must be closed.mbedtls_ssl_get_max_frag_len() may be used to query the active maximum fragment length.