The SysFault driver provides an API to configure the Fault reporting structure. More...
Modules | |
| Macros | |
| Enums | |
| Data Structures | |
| Functions | |
The SysFault driver provides an API to configure the Fault reporting structure.
The functions and other declarations used in this driver are in cy_sysfault.h. You can include cy_pdl.h to get access to all functions and declarations in the PDL. This driver is only available for PSOC 4 HVMS 64/128K, PSOC 4 HVPA 144K, and PAG2S devices.
The fault subsystem contains information about faults that occur in the system. The fault subsystem captures only faults and does not take any action to correct them. The subsystem can cause a reset, give a pulse indication, or trigger another peripheral. HVMS 64/128K, PSOC 4 HVPA 144K, and PAG2S devices use a centralized fault report structure. The centralized nature allows for a system-wide consistent handling of faults, which simplifies software development. Only a single fault interrupt handler is required. The fault report structure provides the fault source and additional fault-specific information from a single set of memory mapped input/output (MMIO) registers, no iterative search is required for the fault source and fault information. All pending faults are available from a single set of MMIO registers. Below is the block diagram.
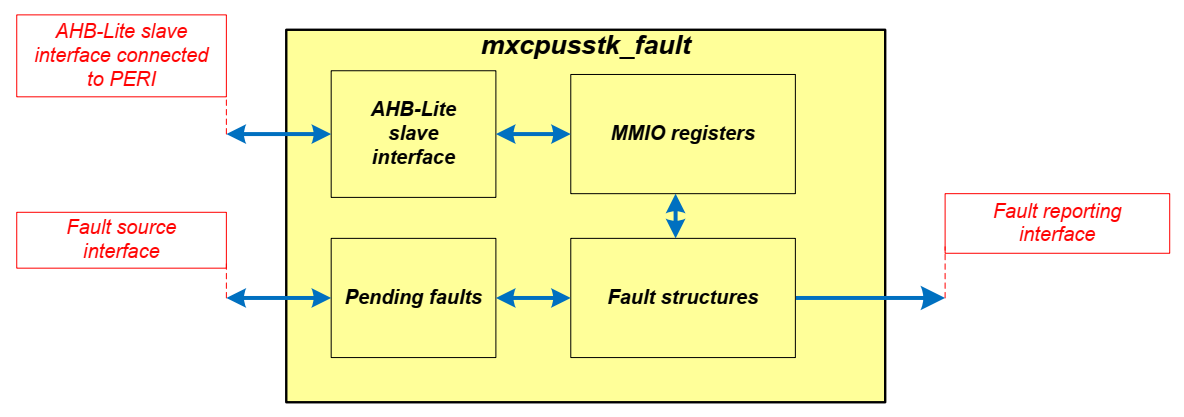
The Fault IP provides a fault report structure. The fault report structures capture faults. The number of fault report structures is specified by the design time configuration parameter (FAULT_NR). In CAT2, there are two instances of fault structures, each fault report structure has a dedicated set of MMIO control and status registers and captures a single fault. The fault report structure provides fault source and additional fault specific information from a single set of MMIO registers. The fault structures capture faults like peripheral specific errors, memory controller specific errors. E.g., SRAM controller ECC errors, FLASH controller read during program and ECC errors, time out errors, power errors.
System fault will be captured by fault report structures. A fault report structure provides the fault source and additional fault specific information from a single set of MMIO registers. The captured fault information includes:
Fault configuration includes the clearing of the existing fault status, enabling the fault source, setting an interrupt mask, and fault initialization. Below is the code snippet for the fault configuration.
Once a configured fault occurs, the interrupt handler will be triggered where the fault information can be captured. Below is the code snippet, which can be part of the interrupt handler.
For more information on the System Fault, refer to the technical reference manual (TRM).
| Version | Changes | Reason for Change |
|---|---|---|
| 1.10 | Added the Cy_SysFault_SetFaultSource and Cy_SysFault_SetFaultData functions. | API improvement. |
| 1.0 | Initial version |