Provides a basic 32-bit lifetime counter with a prescaler (/2 to /32). More...
Modules | |
| Macros | |
| Enumerated Types | |
| Functions | |
Provides a basic 32-bit lifetime counter with a prescaler (/2 to /32).
The functions and other declarations used in this driver are in cy_ltc.h. You can include cy_pdl.h to get access to all functions and declarations in the PDL.
Provides a basic 32-bit up-counter operation in the DeepSleep domain at a frequency lower than Low-Frequency Clock, which can provide a Deep Sleep interrupt when set by FW (match WAKEUP value) or a regular lifetime counter without an interrupt. With the prescaler, the net resolution of the counter becomes 37-bit causing an overflow every 49.7 days. The counter will continue counting upon overflow.
The lifetime counter shall survive all resets except POR/XRES/BOD.
Clock Source
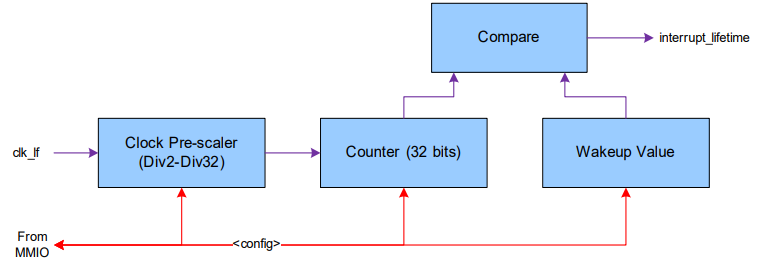
The lifetime counter operates on Low-Frequency Clock. The Low-Frequency Clock release depends on the startup time of the clock. Any AHB writes before Low-Frequency Clock is released will be not pass through to the actual lifetime counter configuration until the Low-Frequency Clock starts. If there is a system reset before the synchronization takes place, the values will be reset, and FW will have to write the configuration again. FW can read the counter value to make sure the counter has started.
The lifetime counter includes a prescaler and is triggered from the Low-Frequency Clock clock. The prescaler provides the Low-Frequency Clock from divide-by-2 up to divide-by-32.
The 32-bit counter runs off of the pre-scaled clock. It is capable of wrapping. The initial value is intended to provide a life-cycle count maintained by software. The value is expected to be loaded after POR by software, and software periodically updates flash to the current count.
Application
Power Modes
The "WAKEUP" value is compared against the hardware "COUNT" value. If there is a match, a Deep Sleep interrupt occurs.
User does NOT need to wait for enable synchronization before entering deepsleep. This will occur within one Low-Frequency Clock cycle. But it is recommended to wait for the enabled status ( Cy_LTC_IsEnabled ) before entering Deep Sleep.
Before using the Cy_LTC_SetDivider or Cy_LTC_SetCounterValue function, disable the lifetime counter by the Cy_LTC_Disable function.
FW shall wait for the counter disabled synchronization before re-enabling the lifetime counter to ensure that the synchronization is completed. The user can read Cy_LTC_IsEnabled to check that the lifetime counter is disabled.
For example:
For more information on the LTC peripheral, refer to the technical reference manual (TRM).
| Version | Changes | Reason for Change |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | Initial version |